O hypertext it is a concept associated with information technologies and that makes reference to electronic writing.
Since its origin, hypertext has been changing the traditional notion of authorship, since it includes several texts.
It is, therefore, a kind of collective work, that is, it presents texts within others, thus forming a large network of interactive information.
In this sense, its biggest difference is precisely the way of writing and reading. Thus, in a traditional text, reading follows a linearity, while in hypertext it is non-linear.
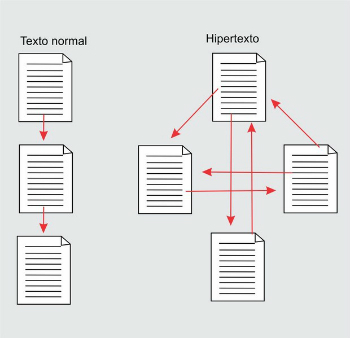
This new way of reading and writing contemplates the various transformations of modern society. In other words, from the proliferation of computers, texts acquire a new interactive dynamic. This is all according to the speed of information we currently receive.
This new multilinear organization of information has been widely used in education. As a way to facilitate understanding, it presents a new text structure: the hypertextual narrative.
The concept of hypertext was created in the 60s by the American philosopher and sociologist Theodor Holm Nelson. The idea was to determine the new non-linear and interactive reading that emerged with information technology and the advent of the internet.
Hypermedia

The hypermedia concept was also created by Theodor Holm Nelson. It is related to the definition of hypertext, as it corresponds to the fusion of media from non-linear and interactive elements.
For some scholars, hypertext is a type of hypermedia. Its difference lies in the fact that hypertext only contemplates texts and hypermedia, in addition, gathers sounds, images, videos.
Hypertext Examples
A strong example of hypertext is articles on the internet. In the body of the text they present several links ("link" in English) or hyperlinks in the words or subjects that are related.
This allows the reader himself to take a more active position, choosing the information he prefers to access.
In addition to internet articles, a storybook, dictionaries and encyclopedias are considered examples of hypertexts.
The information contained in them provides a non-linear character where the reader can also select the information and reading paths they prefer.
Thus, hypertext reading is performed by associations. It does not have a fixed sequence, as occurs in textbooks, novels, chronicles, among others.
Intertextuality and Hypertextuality
Hypertext can be considered a form of intertextuality which, in turn, is a linguistic resource that provides an analogy between at least two texts.
In addition to hypertexts, other types of intertextuality are: parody, paraphrase, epigraph, allusion, pastiche, translation and bricolage.
Thus, the concept of hypertextuality is closely related, as it designates the intertextuality that occurs between hypertexts.
Hypertext in Education

In the field of education, hypertexts have been widely explored in teaching-learning. Its use allows understanding knowledge in an interconnected way, offering an interactive and non-linear information network.
Interdisciplinarity and cross-cutting themes are increasingly gaining ground in educational institutions. Thus, hypertext complements these concepts, since it determines the connection between the different areas of knowledge. This facilitates interactivity between texts, allowing multiple readings.
Through hypertext the reader becomes active (or even a co-author). In this way, he chooses the information and the order he prefers to read, see or listen to, thus creating a relationship between them.
For many researchers, the concept of hypertext came to contemplate the way our brains think, that is, in a non-linear way. This makes education an important aggregator based on the construction of a virtual web of knowledge.
Exercise: Fell in Enem!
With globalization and the advent of the technology era, the concept of hypertext is becoming popular, being increasingly explored in entrance exams, Enem and Contests.
Given its importance, see below a question from the 2011 Enem that addressed the theme of hypertext:
“Hypertext refers to non-sequential and non-linear electronic writing, which bifurcates and allows the reader to access to a virtually unlimited number of other texts from local and successive choices, in time real. Thus, the reader is able to interactively define the flow of his reading based on subjects dealt with in the text without being tied to a fixed sequence or topics established by an author. It is a form of textual structuring that makes the reader simultaneously co-author of the final text. Hypertext is characterized, therefore, as a multilinearized, multisequential and indeterminate electronic writing/reading process, carried out in a new writing space. Thus, by allowing several levels of treatment of a topic, hypertext offers the possibility of multiple degrees depth simultaneously, as it has no defined sequence, but links texts not necessarily correlated.”
(MARCUSCHI, L. THE. Available in: http://www.pucsp.br. Accessed on: June 29 2011.)
The computer has changed the way we read and write, and hypertext can be considered as a new space for writing and reading.
Defined as a set of autonomous blocks of text, presented in a computerized electronic medium and in which there are cross-references associating several elements, the hypertext
a) it is a strategy that, by enabling completely open paths, disfavors the reader by confusing traditionally crystallized concepts.
b) it is an artificial form of writing production, which, by shifting the focus away from reading, can result in contempt for traditional writing.
c) requires a greater degree of prior knowledge from the reader, which is why it should be avoided by students in their school research.
d) facilitates the search, as it provides specific, secure and true information on any search engine or blog offered on the internet.
e) allows the reader to choose their own reading path, without following a predetermined sequence, constituting a more collective and collaborative activity.
Alternative e: allows the reader to choose their own reading path, without following a predetermined sequence, constituting a more collective and collaborative activity.
Read too:
- Textual genres
- Textual Genre Blog
- Textual Genre Email
- Internet history
- History and Evolution of Computers

