At areas of flat figures measure the size of the surface of the figure. Thus, we can think that the greater the surface of the figure, the greater its area.
Plane and Spatial Geometry
Plane geometry is the area of mathematics that studies plane figures. That is, those that have length and width, being two-dimensional figures (two dimensions).
What makes them different from spatial geometric figures is that they have three dimensions and therefore include the concept of volume.
Know more:
- plane geometry
- Spatial Geometry
Main Flat Figures
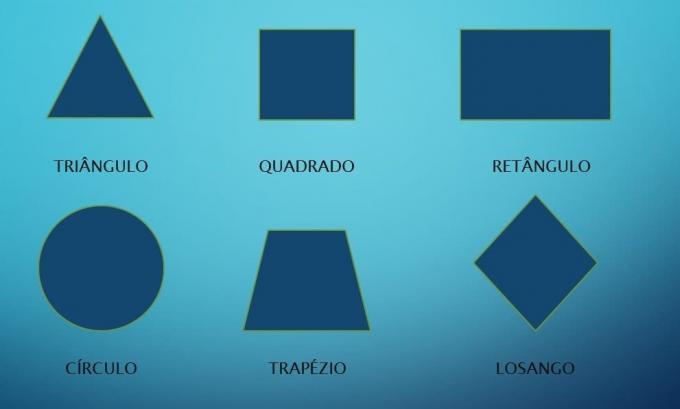
Before presenting the formulas for the areas of the flat figures, we must pay attention to each of them:
triangle: polygon formed by three sides. They are classified according to the measurements of the sides, as well as their angles:
as to side measure:
- Equilateral triangle: has equal sides and internal angles (60°);
- isosceles triangle: has two sides and two congruent internal angles;
- Scalene Triangle: Displays all sides and different internal angles.
as to angle measure:
- Rectangle Triangle: has an internal angle of 90°;
- Obtuse Triangle: has two internal acute angles, that is, less than 90°, and an internal obtuse angle, greater than 90°;
- Acute Triangle: Has three internal angles smaller than 90°.
Read more about triangle:
- Triangle Area
- Triangle Perimeter
- Triangle Classification
- Trigonometry in the Rectangle Triangle
Square: regular quadrilateral formed by four congruent sides (same measure). It is made up of four internal 90° angles, which are called right angles.
Read too:
- Square Area
- Square Perimeter
Rectangle: quadrilateral formed by four sides, two vertically and two horizontally. Like the square, it has four internal 90° (straight) angles.
Read too:
- Rectangle
- Rectangle Area
- Rectangle Perimeter
Circle: Flat figure also called disk. Presents a circular shape. The radius of the circle represents the measurement between the center point of the figure and one of its edges.
The diameter is twice the radius, since it represents the straight line that passes through the center of the circle, dividing it into two equal halves.
Read too:
- Circle Area
- Circle Perimeter
trapeze: remarkable quadrilateral with two sides and parallel bases, where one is larger and the other smaller. The sum of their internal angles totals 360°. They are classified into:
- Rectangle Trapezium: presents two 90º angles (right angles);
- Isosceles trapezius: also called symmetric trapezius where non-parallel sides have the same measurement;
- Scalene Trapeze: all sides have different measurements.
Read too:
- trapeze
- Trapeze Area
Diamond: equilateral quadrilateral formed by four equal sides. It has two congruent and parallel opposite sides and angles, with two diagonals that cross perpendicularly. It has two acute angles (less than 90º) and two obtuse angles (greater than 90º).
Learn more about Diamond Area.
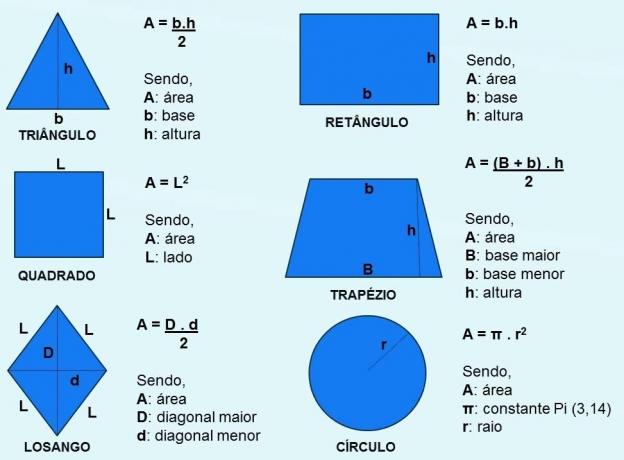
Formula of Flat Figure Areas
Check out the formulas for area calculations below:
See too: Area and Perimeter
Attention!
It is worth remembering that area and perimeter are two concepts used in plane geometry, however, they have differences.
- Area: size of the figure's surface. The area value will always be given in cm2, m2 or km2.
- Perimeter: sum of all sides of the figure. The perimeter value will always be given in cm, m or km.
Know more:
- angles
- Quadrilaterals
- Perimeters of Flat Figures
- Flat Figures Area - Exercises
Solved Exercises
Below are two vestibular exercises on flat figure areas.
1. (PUC RIO-2008) A festival was held in a field measuring 240 m by 45 m. Knowing that for every 2 m2 there were, on average, 7 people, how many people were there at the festival?
a) 42,007
b) 41,932
c) 37,800
d) 24,045
e) 10,000
To find out how many people were at the festival, we must first find the area. From the description, the place has a rectangle shape:
A = b. H
A = 240. 45
A = 10 800 m2
So if every 2 m2 there were, on average, 7 people, we know that in 1m2 there were about 3.5 people.
Therefore, the measure of the area is multiplied by the number of people in each house m2.
10.800. 3,5 = 37.800
Alternative C
2. (UFSC-2011) A cyclist usually makes 30 complete laps a day in the square block where he lives, whose area is 102400 m2. So, the distance he cycles per day is:
a) 19200 m
b) 9600 m
c) 38400 m
d) 10240 m
e) 320 m
If the area of the block is 102400 m2 , we can figure out the value of its side once we know it's square.
So, if we calculate the area of the square, we use the formula:
A = L2
102400 = L2
√ 102400 = L
L = 320 m
Now that we know the measure of each side of the block, we can figure out its perimeter, that is, the sum of all sides. If the square has 4 sides, we can multiply the value by 4:
P = 320. 4
P = 1280 m
Thus, if the cyclist runs 30 complete laps per day, he runs 30 times the perimeter value:
30.1280m = 38 400 m
Alternative C.
Check out more issues, such as commented resolution, at Area and Perimeter Exercises.