Oxygenated Functions are one of the 4 functional groups of organic compounds. The compounds that belong to this function are formed by oxygen, being Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Ethers, Phenols and Alcohols.
alcohols
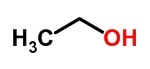
You alcohols they are formed by hydroxyls linked to carbons that carry out only single bonds.
Alcohols can be primary, secondary or tertiary.
- Primers when attached to just one carbon atom
- Secondaries when bonded to two carbon atoms
- tertiary when attached to three carbon atoms.
The main alcohols are ethanol, present in alcoholic beverages and fuel, and methanol, which is used as a solvent.
Its nomenclature follows the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, in Portuguese):
- prefix - number of carbons
- intermediate - type of chemical bond
- suffix - ol, of alcohol
esters

You esters are very similar to carboxylic acids. That's because the only difference between them is that esters have a carbon radical, while carboxylic acids have hydrogen.
These organic compounds can only be dissolved in alcohol, ether and chloroform.
Esters are flavoring, meaning they are used to flavor substances such as sweets, juices and syrups.
The name of the esters is formed as follows:
- the prefix indicates the number of carbons
- the intermediate indicates the type of chemical bond
- the suffix -oato is added, as is the element "from"
- follows the ending -ila
Aldehydes
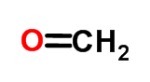
You aldehydes they consist of aliphatic or aromatic organic compounds. They have a carbonyl composition (double C O), which is located at the ends of the molecular structure.
As aldehydes present in everyday life we can mention disinfectants, medications, plasticizers, resins and perfumes.
The main ones are Methanal (Formaldehyde), Ethanal (Acetaldehyde), Propanal (Propionaldehyde), Butanal (Butyraldehyde), Pentanal (Valeraldehyde), Phenyl-Methanal (Benzaldehyde) and Vanillin.
According to IUPAC, -al is its suffix used to name compounds. This suffix indicates the organic function of the aldehydes.
Ketones

At ketones they are composed of carbon in a double bond with oxygen, the carbonyl, which is found in the middle of the molecule.
Ketones can be symmetrical (identical radicals) or asymmetrical (different radicals).
They are classified according to the number of carbonyls: monoketones (1 carbonyl), polyketones (2 or more carbonyls).
Ketones are used as solvents, including to remove nail polish.
According to IUPAC, -one is its suffix, which indicates the organic function of ketones.
Phenols
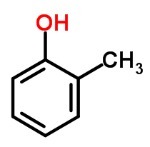
You phenols they are composed of carbon and hydrogen bonded to hydroxyls.
They dissolve in alcohol and ether and most of them are corrosive and toxic. They are classified according to the number of hydroxyls they present: monophenols (1 hydroxyl), diphenols (2 hydroxyls) and triphenols (3 hydroxyls).
They are used in the manufacture of explosives, bactericides, fungicides and creoline.
ethers
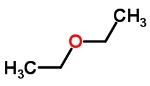
You ethers are very flammable compounds formed by oxygen between two carbon chains. They can be found in liquid, solid and gaseous states and have a very strong smell.
They can be symmetrical (identical radicals) or asymmetrical (different radicals).
Ethers are used as solvents.
The prefix indicates the number of carbons, just like the rest of the compounds. However, the oxygen side that has the least carbon suffix is -oxy, while the oxygen side that has the most carbon suffix is -year.
Carboxylic Acids
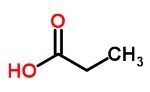
Weak acids formed by carboxyl, which often have an unpleasant smell.
It is present in vinegar (ethanolic acid), in perspiration, in fruits (ascorbic acid).
You carboxylic acids they can be aliphatic, when its chain is open, or aromatic, when there is an aromatic ring.
They are classified according to the number of carboxyls they have: monocarboxylic (1 carboxyl), dicarboxylic (2 carboxyl) and tricarboxylic (3 carboxyl).
According to IUPAC, -oic is its suffix, which indicates the organic function of carboxylic acids.
Read too Organic Functions.
Entrance Exam Exercises with Feedback
1. (Mackenzie-SP) About ethanol, whose structural formula is H3C CH2 ─ OH, identify the wrong alternative:
a) has a saturated carbon chain.
b) is an inorganic base.
c) is soluble in water.
d) is a monoalcohol.
e) presents a homogeneous carbon chain.
Alternative b
2. (UFRN) The compound that is used as orange essence has a formula:
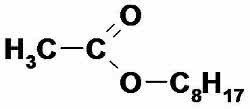
a) methyl butanoate.
b) ethyl butanoate.
c) n-octyl ethanoate.
d) n-propyl ethanoate.
e) ethyl hexanoate.
Alternative c
3. (UFU-MG) The correct name of the compound below, according to IUPAC, is:
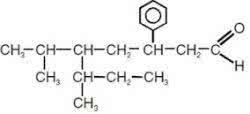
a) 3-phenyl-5-isopropyl-6-methyl-octanal
b) 3-phenyl-5-sec-butyl-6-methyl-heptanal
c) 3-phenyl-5-isopropyl-6-methyl-octanol
d) 2-phenyl-4-isopropyl-5-methyl-octanal
e) 4-isopropyl-2-phenyl-5-methyl-heptanal
Alternative to
4. (U. Católica de Salvador – BA) Ketone is a carbonyl compound with 3 carbon atoms and saturated chain. Its molecular formula is:
a) C3H6O
b) C3H7O
c) C3H8O
d) C3H8O2
e) C3H8O3
Alternative to
5. (PUC-PR) About 3-phenyl propanoic acid, it is correct to state that:
a) has molecular formula C9H10O2.
b) has a quaternary carbon atom.
C) has 3 ionizable hydrogen atoms.
d) is not an aromatic compound.
e) is a saturated compound.
Alternative to



