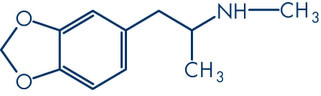
The substance that defines the ecstasy it's the 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, better known by the acronym MDMA. Its structural formula is shown below, being a compound amphetamine derivative, that is, synthetic substances belonging to the amine group that act on the nervous system, stimulating it.
However, ecstasy is not part of the amphetamine group. To better understand this group and verify its distinction with ecstasy, read the text “Amphetamine Chemistry”.
MDMA has part of its molecule similar to a hallucinogen, however, it does not produce lysergic acid (LSD) hallucinations, nor the stimulant effects of cocaine. Its effects are like a mild mixture of the two substances.

Its use is illegal and causes numerous adverse reactions, which can even lead to death. The biggest cause of death associated with the use of ecstasy is hyperthermia, that is, an increase in body temperature, which causes overheating.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
This is because ecstasy acts on the brain's neurotransmitters (serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine). The one that is most influenced by this drug is serotonin, responsible for controlling emotions, regulating the sensory and motor domains, the associative capacity of the brain and also regulate the temperature of the body. With ecstasy achieving this serotonin function, the body can reach temperatures above 41°C, causing the blood to clot, producing seizures and cardiac arrest.
Other side effects of using this drug are: headaches, muscle pain, nausea, toxic hepatitis, kidney problems, cardiac arrhythmia, hallucinations and panic attacks.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Chemistry of Ecstasy"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/quimica-ecstasy.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Amines, classification of amines, amine properties, primary amine, nitrogenous organic compounds, alkyl radicals, dimethylamine, ethylamine, trimethylamine, compounds extracted from vegetables, putrescine, cadaverine, organic bases, syntheses organic
Chemistry

Caffeine, Amphetamine, Cocaine, Crack, amines, increased nervous system activity, reduced appetite, caffeine, intense depression, hydrochloride, motor activity, guarana powder.
Chemistry

How does electronic cigarette work, toxic substances, pure nicotine, cadmium, arsenic, vaporization chamber, reducing smoking, cigarette without tobacco, alternative for those who want to quit smoking.
Chemistry

Synthetic Substances, methylene-dimethoxy- methamphetamine, strongly psychoactive substance, ecstasy, MDMA, saccharin, cyclamate, plastics, acrylic, detergents, natural rubber, organic rubbers, synthetic rubber, hydrocarbons synthetics, pulley