Adsorption is a physicochemical property of molecules of liquid, gaseous and solid substances.
The process occurs when liquid or gaseous particles are trapped on the surface of solids. If the solids are porous, the adsorption capacity increases even more.
There are two classifications for the components that participate in the process:
- Adsorbates: It is the liquid or gaseous substance that is retained on the surface of an adsorbent solid.
- Adsorbents: It is the solid substance that promotes the retention of other substances.
THE desorption it is the inverse process of adsorption, that is, it is the release of adsorbate from the surface of the adsorbent.
Types
Depending on the nature of the forces involved in the process, adsorption can be of two types: physisorption and chemisorption.
In some cases, both types of adsorption can occur in the same process.
physisorption
The physical physisorption or adsorption between the adsorbate and the adsorbent occurs through Van der Waalls forces (dipole-dipole or induced dipole).
In this case, there is no type of molecular change in the substances involved in the process. That is, the substance retains its chemical nature.
Physical adsorption is a reversible process.
Chemisorption
Chemisorption or chemical adsorption consists of a chemical reaction. By involving the electrons, is considered a stronger chemical bond than physisorption.
In chemisorption, there is a molecular alteration of the substances involved in the process. That is, the substance can be transformed into another.
As this is a chemical reaction, the components of the adsorbent and the adsorbate must have specificity. They must be able to recognize and react.
Chemical adsorption is an irreversible process.
Also read about:
- Intermolecular Forces
- Chemical bonds
Adsorption and Absorption
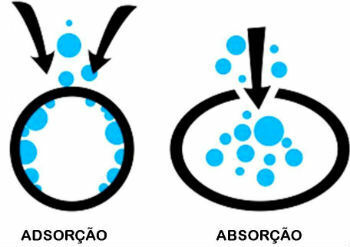
Difference between adsorption and absorption
Adsorption and absorption are two distinct processes. Know the difference between them:
- adsorption: A substance is retained on the surface of another, however, without being part of its volume.
- Absorption: One substance is imbibed by another, causing a change in volume.
A common example of absorption is the sponge that absorbs water. By doing this, the volume of water is incorporated into the volume of the sponge.
Activated charcoal
Activated carbon is an example of a better known adsorbent substance. In its structure there are numerous pores that intensify the retention of substances and increase their adsorption capacity.
Therefore, activated carbon is used to remove organic substances, oils, colors and odors. It is also used for water treatment and the manufacture of cosmetics and medicines.

Activated charcoal
Read too:
- Chromatography
- Separation of mixtures
- Solute and Solvent
- Materials used in the Chemistry laboratory


