THE distillation, in general, is one of the most used methods for break apart the components of homogeneous mixtures that present liquid with solid or only liquids in their composition.
The call fractional distillation it is used exclusively to separate the components of a mixture that has two or more liquids in its constitution, such as a mixture of water and acetone. It is important that the liquids that make up the mixture do not have boiling points that are too close or that the mixture is not azeotropic (homogeneous mixture formed only by liquids that has a boiling point constant). In these two cases, chemical methods are required for the separation to take place.
Equipment used in a fractional distillation they are practically the same as for a simple distillation, with the addition of equipment called a fractionation column. See all of them below:
Iron tripod: supports the asbestos screen and glass balloon;
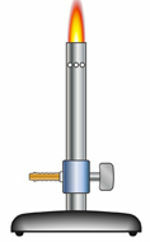
Bunsen burner: equipment that performs the heating of the mixture;
-
Asbestos screen:
equipment that is positioned on the tripod so that it absorbs part of the heat coming from the bunsen burner, preventing the distillation balloon from bursting;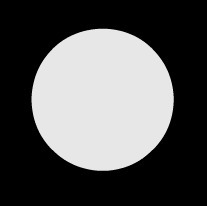
Observation: the asbestos screen set, iron tripod and bunsen burner can be replaced by an electric heating plate.
Glass balloon:glass equipment that receives the homogeneous mixture composed of liquids;

Fractionation column:glass tube filled with glass or porcelain marbles.

Condenser: equipment where the vapor is transformed into a liquid.

Erlenmeyer or any other collecting tube: glass equipment that receives the liquid that has been condensed in the condenser.

Thermometer:equipment that allows monitoring the temperature during the distillation process.

How a fractional distillation works is based on the difference of boiling point between the liquids that make up the mixture. Let's use the example of water (boiling point equal to 100 OC) and acetone (boiling point equal to 58 OC) to understand how this process works.
Initially we add the mixture to the glass flask. We then turn on the bunsen burner or the heating plate to heat the mixture. From there, the two liquids begin to transform into vapor and move towards the fractionation column, where they compete for the same space. As the fractionation column is an obstacle, as it contains several balls and little free space, only one of the vapors is able to cross it. Only the liquid vapor that has the lowest boiling point passes through the fractionation column, since the lower the boiling point, the lower the vapor density. After passing through the fractionation column, the liquid vapor with a lower boiling point enters the condenser and undergoes the phenomenon of condensation, returning to the liquid state. Finally, the condensed liquid is collected in the collecting flask. The following image shows a fractional distillation scheme:
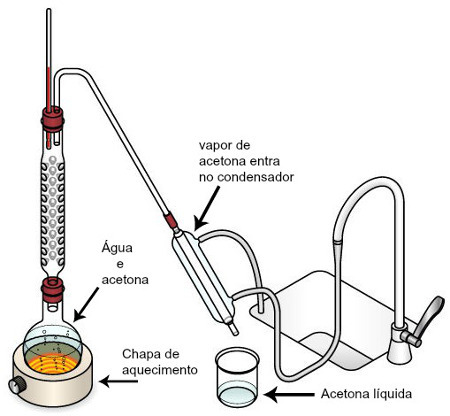
Fractional Distillation Illustration
As in the example used, acetone has the lowest boiling point, it is the one that manages to cross the fractionation column, being condensed and collected in the collector flask.
Observation: To prevent water vapor from also passing through the fractionation column, it is important to always stay on eye the thermometer and do not allow the heating temperature to exceed the value of the lowest point of boiling.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/destilacao-fracionada.htm
