O muscle tissue features cells elongated capable of contracting. It is responsible for forming our muscles, important structures for our movement, for ensuring the transit of food through the pipe digestive, for promoting the beat of the heart, among other functions. Next, we'll find out more about muscle tissue, its types and its importance.
Read more:Human body tissues - general characteristics and main differences between them
Muscle Tissue Characteristics
O muscle tissue, as said, stands out for presenting elongated cells (which are also called muscle fibers) capable of contraction. This is due to the presence of filaments of proteins for example, actin and myosin.
Muscle tissue cells are eukaryotes typical, that is, they have a well-defined membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus, in addition to the presence of organelles membranous. These cells, however, have specific names. THE plasma membrane, for example, is called sarcolemma; the cytoplasm, from sarcoplasm; and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, the sarcoplasmic reticulum.

Although we say that muscle tissue has elongated and contracting cells, it is important to emphasize that not all muscle tissue is identical. Some have transverse striations, others do not. Some have cells with multiple nuclei, while others have only one nucleus.
These variations allowed classifying the muscle tissue into three types distinct: skeletal striated muscle tissue, non-striated muscle tissue and cardiac striated muscle tissue.
Skeletal striated muscle tissue
Features long, cylindrical cells with multiple nuclei. The multiple nuclei of cells in this type of tissue are arranged more on the periphery, that is, close to the plasma membrane (sarcolemma). Each muscle fiber has bundles of filaments called myofibrils, which are repetitive arrangements of sarcomeres, considered the contractile unit of a skeletal striated muscle.
As the name suggests, this fabric features transverse striations. They occur due to the repetition of the sarcomeres, with an alternation between light and dark bands being observed. THE light band is called band I and is made up of thin filaments (actin). THE dark band, in turn, is called the A-band and is formed by thick (myosin) and thin filaments.
We can still perceive the presence of the Z line, a dark transverse line in the center of band I. Band A also has a distinct region in its center, it is band H, which stands out for being clearer.
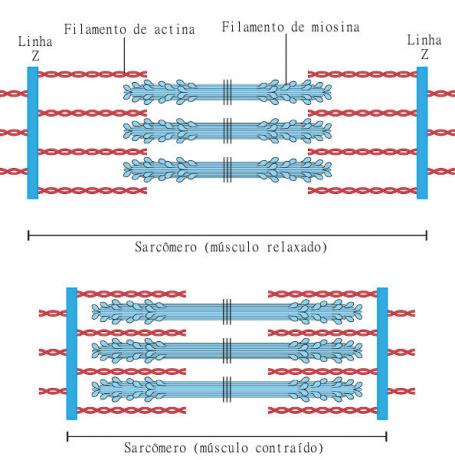
O sarcomere is delimited by the Z lines. Thus, it is formed by two I semibands, with an A band separating them, and this whole set is delimited by Z lines. In muscle contraction, a series of processes occur that ensure the sliding of the filaments over each other, causing the sarcomere to shorten.
THE contraction of skeletal muscles is quick and voluntary, being found attached to the our bones. It is important to point out that, despite being a voluntary muscle, there may be involuntary contractions, such as reflexes.
Non-striated (or smooth) muscle tissue
Does not have striations, a characteristic present in the other two types of muscle tissue. Its cells are spindle-shaped, that is, they are thicker in the center and attenuated at the ends. They do not have multiple nuclei like striated skeletal muscle tissue, and it is possible to observe only a single, central nucleus.
This type of muscle tissue is found forming the wall of several hollow organs in our body, for example, the stomach, at arteries, O uterus, the bladder, among others. Yours contraction occurs involuntarily, not being induced by the individual, and is slower than in other tissues.
Cardiac striated muscle tissue
It is present in the heart, being responsible for promoting the contraction of this organ and, consequently, the boosting of the blood. this fabric has striations, its cells are long, have one or two nuclei located in the center of the cell, and are distinguished by the presence of branches at the ends.
The striated cardiac muscle tissue cells unite through structures called the insert discs. These discs are unique to this tissue type and are important to ensure that the cells do not become separate at the time of the heartbeat and to allow the transmission of signals from one cell to another.
Muscle Tissue Functions
Muscle tissue is found in various parts of our body, and its contraction is essential for carrying out several important processes. Among the main roles played by him, we can mention:
Movement of our body;
Heat production due to muscle contraction;
Food movement through the digestive system;
Movement of blood through blood vessels;
Contraction of the heart and, consequently, boosting the blood;
Guaranteed increase in the size of organs and their subsequent return to normal size.
Read too: Is the skin a tissue or an organ?