O blood it is a liquid connective tissue, red and viscous in color, which runs inside our blood vessels. for being a fabric, é made up of different types of cells, which are suspended in a liquid matrix. We will talk more about blood below, highlighting its function in the body and its components.
Blood Functions
blood is a fluid tissue that moves by Cardiovascular system and that features a big variety of functions. Among these functions, the one of transport, being the blood responsible for transporting nutrients, respiratory gases and also metabolic wastes. In addition, this fabric is related to the coagulation, due to the action of platelets, and with the body's defense, due to the action of leukocytes.
Where does blood production take place?
Blood is produced in the bone marrow, more precisely in the so-called red bone marrow. The first is located in the spinal canal of certain bones. The second is present inside the vertebrae, in the rib, in the sternum and in the cancellous tissue layer of the skull bones. If you are more interested in the topic, read our text: How is blood produced?
Know more:Leukemia, a disease that affects the bone marrow
blood components

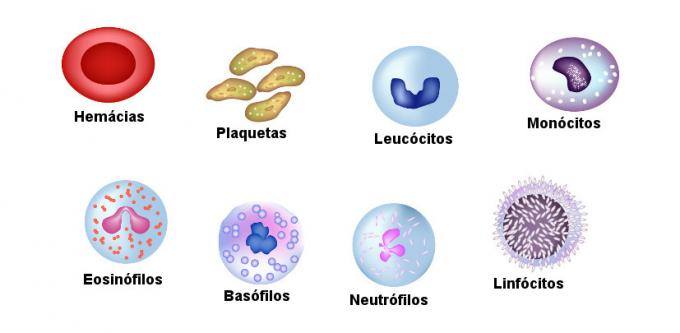
The blood is composed by theplasma, which is a liquid matrix, and by cellular elements, which include cells and cell fragments. See more about these components:
Blood plasma
It is the liquid part of the blood corresponding to about 55% of its total volume. It is basically formed by Water and some dissolved substances, showing a yellowish color. Among the substances found in plasma, we can mention glucose, hormones and vitamins, in addition to ions, such as sodium and potassium, and proteins, such as antibodies.
Cell elements
Also called figurative elements, they refer to blood cells and platelets, which are actually fragments of cells. These elements constitute about 45% of the total blood volume and are these:
Red Cells: also called red blood cells or erythrocytes, they are blood cells that have a biconcave disc shape (thinner in the center) and do not have a nucleus, that is, they are anucleate. Inside this cell, a large amount of hemoglobin is found, a red pigment that is related to the transport of oxygen, and also carbon dioxide.
Red blood cells are the most numerous cells in the blood and, as they are rich in hemoglobin, they are responsible for ensuring its characteristic red appearance. Red blood cells live for a short time: 120 days.
There are about 25 trillion red blood cells in five liters of blood in the human body. |
Leukocytes:also called blood cells, they are colorless cells, larger than red blood cells, and their main function in the body is to guarantee the body's defense. For this, they act in different ways, the main ones being: the production of antibodies and phagocytosis.
Antibodies are defense proteins and are produced by specific leukocytes. Phagocytosis, on the other hand, is a process in which a cell engulfs and digests the foreign particle. (See drawing below.)

There are five basic types of white blood cells (lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils), which are grouped into two groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes.
In the first group, we have leukocytes with an irregular nucleus and presence of specific granules; the calls are part of it neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. In the second group, we have leukocytes with a more regular nucleus and without the presence of granules. You lymphocytes and monocytess are classified that way.
You see an increase in the number of white blood cells in the body every time we are fighting an infection. |
Platelets:also known as thrombocytes, they are not whole cells but fragments of cells called megakaryocytes. Platelets do not have a nucleus and their shape is like a small disk. Furthermore, they are related to the process of repairing blood vessels and blood clotting.
Cellular elements of blood | ||
Cell component |
Occupation |
Quantity per microliter of blood |
Red Cells |
Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide |
5,000,000 to 6,000,000 |
Leukocytes |
organism defense |
5,000 to 10,000 |
platelets |
Blood clotting and blood vessel repair |
250,000 to 400,000 |
See too:Antibodies and our body's defense
blood related diseases
Here are some diseases that are related to blood:
Anemia:it is characterized by a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin present in the blood. It can be triggered, for example, by the loss of a large amount of blood, the production of red blood cells with little hemoglobin or even a small production of red blood cells. A diet low in iron may be responsible for reducing the level of hemoglobin in the body.
Hemophilia: it is a genetic problem related to a deficiency in one of the coagulation factors, which triggers a defect in this process. Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe. In the latter case, it is common to see bleeding in the individual even without any trauma.
Leukemia: it is a type of cancer that affects our body's defense cells, ie, leukocytes. According to the National Cancer Institute, in this disease, a cell that is not yet mature undergoes a mutation and turns into a cancer cell, which does not function properly, multiplies rapidly and dies less than the normal cells. These cells then replace healthy cells. It is noteworthy that there is not only one type of leukemia, with more than 12 different types being known.
Read too:Cancer - factors and main treatments
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson on the subject: