Surrounding planet Earth is a layer of gases we call the atmosphere. The sun's rays pass through, heating the earth's surface which, when heated, releases heat. A part of this heat is absorbed by the atmosphere and the other part is lost in space. When the atmosphere absorbs this heat, it doesn't allow the Earth to cool down much and keeps the Earth's surface warm, making life on Earth possible. If that didn't happen, the Earth would be very cold, around -270C, and it would be impossible to live here. This is what we call greenhouse effect, a natural process.
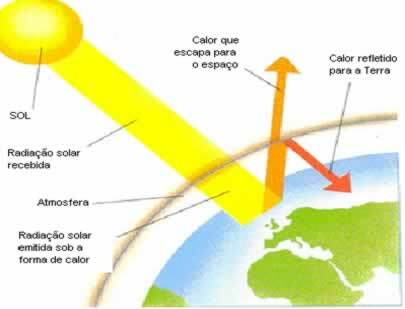
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon
Burning in forests and forests, industries, factories and gasoline and diesel engines emit various gases, including CO2 (carbon dioxide). These gases reach the atmosphere and form a layer preventing much of the heat inside the Earth from escaping. What happens is an increase in the temperature of the Earth's surface, the so-called global warming.
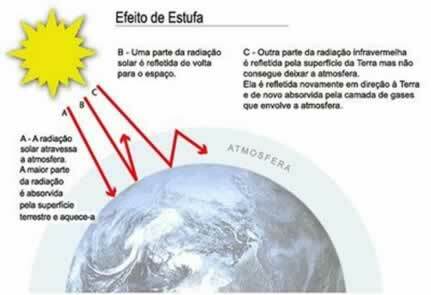
CO2 forms a barrier that prevents heat from leaving the Earth
As a consequence of this increase in temperature inside the Earth, we can see the melting of the polar ice caps, causing an increase in the level of the oceans; the decrease in air humidity, which can cause desertification in some regions; the increase in hurricanes, typhoons and tornadoes and intense heat waves.

Consequences of the greenhouse effect
So that the greenhouse effect does not become a problem, society needs to reduce air pollution, but how can we do this?
• Planting more trees;
• Avoiding fires;
• Recycling garbage;
• Using solar energy and wind energy (wind) to produce electricity;
• Using more public transport;
• Placing filters in industries and factories;
• Decreasing CO2 emission by means of transport;
• Making the world population aware of global warming.
Paula Louredo
Graduated in Biology