Coulomb's Law deals with electrostatic relationships between particles that are electrically charged. It was created by French physicist Charles Coulomb (1736-1806) in the 18th century.
From the observation of the behavior of electrostatic particles, Coulomb realized that they have two distinct characteristics: attraction or repulsion. These properties manifest themselves according to the force of attraction of the particles.
What is Coulomb's Law?
Simply put, the law states that there is an attractive force between electrical charges of opposite signs and a repulsive force between charges of equal signs.
When determining the law, Coulomb also pointed out that the forces with which the particles interact are of the same intensity.
Thus, Coulomb's Law is the observation of the relationship that exists between the charge of bodies and the (electrical) force that occurs between them, according to their charge.
Coulomb's analysis was essential to determine the electrical force produced by electrical charges. The strength can be discovered using the Coulomb's Law formula.
Coulomb's Law Formula
The Coulomb Law equation states that:
- The force between charged particles (q1 and q2) will be directly proportional to the value of your charges.
- The force between the particles (q1 and q2) will be inversely proportional the square value of the distance between them.
Observe the Coulomb's Law formula for obtaining electrical force:
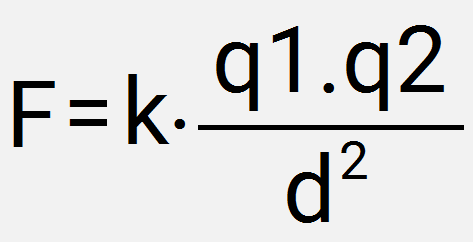
In the formula:
- F: strength (in Newtons -N).
- k: electrostatic constant (in N.m2/Ç2).
- q: electric charge (in Coulombs - Ç).
- d - distance (in meters - m).
Attraction and repulsion forces
As we have seen, the forces are determined according to the electrical charges of the analyzed particles. When using the formula, you need to look at the results to determine whether the forces are of attraction or repulsion.
- If (q1.q2) is less than zero: force of attraction.
- If (q1.q2) is greater than zero: repulsion force.
What are electrical charges?
These are the particles that make up atoms and can be of three types: positive (protons), negative (electrons) or neutral (neutrons).
Particles are measured in Coulomb (C), in reference to the physicist who created Coulomb's Law.
Also read the meaning of electric field.


