Ribosomes are small structures present in cells, responsible for cell protein production through the genetic information carried in the messenger RNA.
They are cell organelles, microstructures present in cells that perform specific functions to ensure cell function.
Ribosomes are shaped like granules, similar to small grains. Are present in the cells prokaryotes (simple unicellular organisms) and in eukaryotes (unicellular or multicellular organisms with nuclear membrane).
They are located in various regions of a cell, but mainly in the cytoplasm. They can also be found in other parts of the cell, such as mitochondria and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
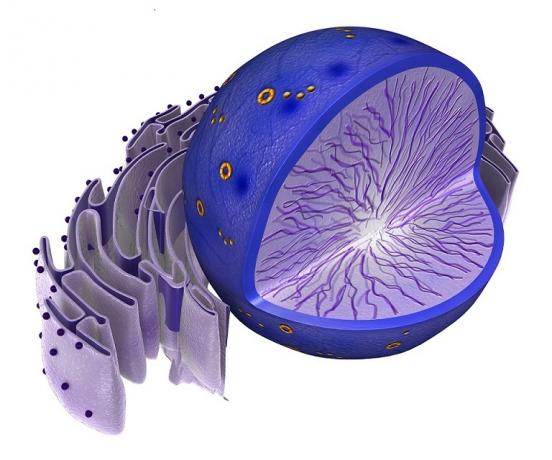 The blue dots are the ribosomes. They are free in the cytoplasm, but they can also exist in other parts of the cell.
The blue dots are the ribosomes. They are free in the cytoplasm, but they can also exist in other parts of the cell.
What is the function of ribosomes?
The main function of ribosomes is to produce protein in cells, that is, to make the protein synthesis. The production of proteins happens with the joint action of ribosomes, enzymes, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
Proteins are essential for cells and for ensuring the proper functioning of the body. They play a variety of functions, such as: acting in hormonal balance, in the production of antibodies and in the health of muscles and tissues.
How does protein synthesis take place?
Protein synthesis takes place through the transcription of a coded genetic coding contained in messenger RNA. Production is completed after performing two steps: transcription and translation.
At transcription, the codes of a DNA molecule are transcribed into a messenger RNA molecule. In this phase, the messenger RNA nitrogen base pairing occurs:
- adenine (DNA) and uracil (RNA),
- thymine (DNA) and adenine (RNA),
- cytosine (DNA) and guanine (RNA).
This sequence of bases will form an amino acid coding called a codon.
At Translation the decoding of the messenger RNA message, contained in the codon, takes place.
The messenger RNA molecule repeats the message contained in the DNA, which will give rise to the protein. This information is used by the ribosome to finalize protein synthesis.
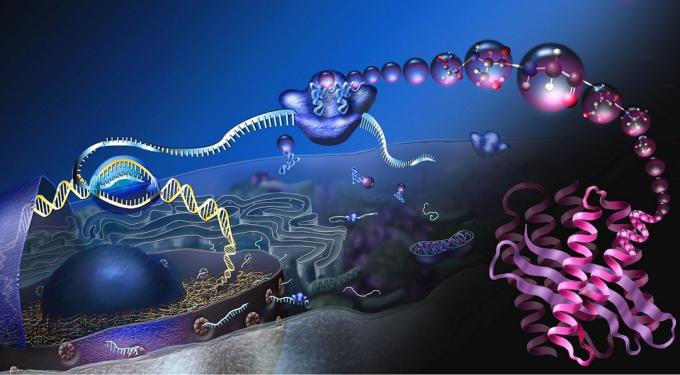 Protein production: the ribosomes present in the cytoplasm form a chain of amino acids that give rise to the protein.
Protein production: the ribosomes present in the cytoplasm form a chain of amino acids that give rise to the protein.
Read more about the importance of proteins.
Structure and composition of a ribosome
Ribosomes are made up of RNA, also called ribosomal RNA. They have two parts of different size - both formed by RNA and proteins - that together fulfill the important function of protein synthesis.
For the ribosome to be able to fulfill this function, its halves must be connected and work together.
Its size can vary between 20 and 30 millimeters, depending on the type of cell in which it is found. They are usually smaller in prokaryotic cells.
Know more about DNA and RNA.
Features
See the summary of the main characteristics of ribosomes:
- are cytoplasmic (have cytoplasm),
- are formed by RNA and proteins,
- they are shaped like small grains, being rounded,
- they are made up of two parts of different sizes.
See also the meanings of prokaryote, eukaryote and cell.

