Thermal energy is a form of energy that is related to high temperatures and heat.
Thermal energy is formed as a result of kinetic energy (movement) of molecules and particles in a given body.
The greater the movement of these particles, the higher the temperature and, consequently, the more intense the thermal energy released.
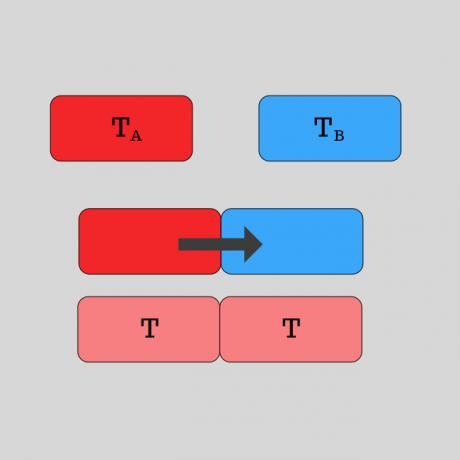
Heat is precisely the transmission of thermal energy from one body to another. This process can be done through radiation, driving or convection.
Thermodynamics is the research area responsible for studying thermal energy.
In a practical example, according to the principles of Thermodynamics, when two bodies with different temperatures are in contact, after a certain time, it is noticed that both temperatures are equal.
The higher-temperature body transfers heat, that is, thermal energy, to the lower-temperature body.
Benjamin Thompson and James Prescott Joule were some of the pioneers in this field of study. By the way, joules (J) came to be used as the name of the unit of measurement when it comes to heat as energy, according to the international system of Thermodynamics.
At thermoelectric plants produce electricity based on thermal energy. This process requires the use of combustible raw materials (such as oil, gasoline, natural gas or coal).
Advantages of thermal energy
- It can be obtained from the sun (solar energy), not polluting the environment.
- Obtained from burning wood, a cheap raw material found anywhere.
- It can be obtained through natural gas, which is less polluting than oil and coal derivatives.
- It is a quick and cheap alternative for the production of electricity, compared to hydroelectric plants, for example.
Disadvantages of thermal energy
- The burning of fossil fuels, used to obtain this energy, causes a lot of pollution.
- Release of large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Helps to increase the greenhouse effect.
- It causes deforestation and unconscious felling of forests to extract wood.
See also the meaning of Nuclear energy.