The living beings are organisms that have a set of elements existing in its composition, which do not exist in gross, lifeless matter.
To be considered living beings, these organisms share important characteristics in common, which unfold into others, according to their complexity.
The main characteristics of living things are:
1. have DNA
The first characteristic of a living being, when compared to a being that has no life, is its complex chemical composition.
A living being is that organism that has nucleic acid, formed by DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). Nucleic acid is responsible for human genetic material and for the transmission of hereditary characteristics. This is a composition that we find exclusively in living beings.
DNA and RNA have different functions. DNA contains the genetic information of a living being, produces RNA and controls cell activity.
RNA, on the other hand, makes the synthesis of proteins in the body and sends genetic information so that the synthesis of proteins takes place in the cells.
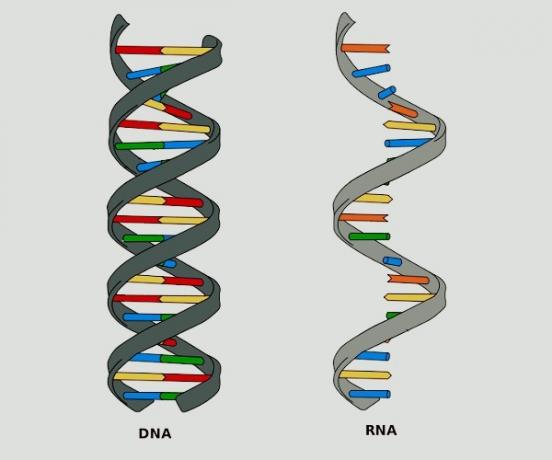
DNA and RNA strands.
All living organisms have organic elements such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen in their composition. They also have inorganic compounds such as water and mineral salts.
We can also find phosphorus and sulfur in the composition of a living being, but in smaller amounts.
know more about DNA and RNA.
2. Go through the life cycle
Every living being goes through a life cycle, in which he is born, grows, reproduces and dies. Although some species may not complete the entire cycle, it is an important feature of a living organism.
In the adult phase, living beings need to reproduce, that is, generate new living beings with characteristics similar to themselves, as a way to guarantee the continuity of their species.
Reproduction can take place in an asexual or sexual way. reproduction asexual it happens when an organism splits into two or more parts that give rise to new organisms. Asexual reproduction is common in unicellular living beings.
Already the reproduction sexual it happens from the formation of special cells called gametes, which originate from the crossing between a male and a female gamete. Sexual reproduction takes place in multicellular beings.
3. Are formed by cells
Another important characteristic of living beings is their cellular organization. All living organisms, except viruses, are made up of units known as cells.
Basically the cell structure is formed by cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus.

Cells can be prokaryotes or eukaryotes. They are prokaryotes when they do not have the plasma membrane that separates the cell material from the cytoplasm. They are eukaryotes when there is this nuclear membrane.
Chromosomes are located in the cell nucleus, where the DNA with genes responsible for transmitting the hereditary characteristics of living beings is located.
Regarding cells, living beings can also be classified into:
- single cell: are beings formed by a single cell, such as monera (bacteria and cyanobacteria), protists (protozoa and algae) and some fungi,
- multicellular: they are beings formed by several cells, such as animals, plants and fungi in general.
See more about Cell and DNA.
4. Grow according to your adaptation
In order to grow, living beings remove the necessary nutrients from the environment for their survival and, in this way, their cells increase in volume, multiplying and increasing even more the body.
But in order to survive, living beings also need to adapt to different situations. For example: they can react to environmental stimuli such as light, sound, they can move, produce hormones, among others.
When a living being is born, the phenomenon of mutation, which is the alteration of one or more genetic characteristics. Mutations are caused by a change in one or more genes or by a change in their chromosomes.
If the mutation happens in cells that participate in the formation of embryos, it can be transmitted to the offspring through reproduction. For this reason, mutation can explain the emergence of new species of living beings and the evolution of some that already exist.
5. Do the metabolism process
After being born, the living being undergoes constant chemical reactions in its body, in which the molecules simple molecules are transformed into more complex molecules from a synthesis reaction with the expenditure of energy. This process is called anabolism.
These molecules can also be broken down, becoming simpler molecules again, causing the catabolism. In catabolism, a reaction called degradation takes place, in which the body receives energy.
Anabolism and catabolism are different phases of biochemical reactions responsible for chemical changes in cells.
These two processes together form the metabolism, which is necessary for the living being to continue in constant evolution and growth.
See more about the Metabolism, Evolution and meet the difference between anabolism and catabolism.
6. Produce energy through nutrition and breathing
For a living being's metabolism to work properly, the body needs to consume a large amount of energy. This energy comes from two sources: through nutrition and breathing.
Nutrition
In relation to the form of nutrition, organisms can be autotrophs or heterotrophs. the organisms autotrophs they are those who produce their own food, mainly through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis (plants and vegetables, for example).
THE photosynthesis it is the process of absorbing water and carbon dioxide, which are transformed into energy (glucose). In this process, which is done through chlorophyll and energy from sunlight, the air is purified by releasing oxygen.
THE chemosynthesis it is a process of synthesis (decomposition) of organic compounds, which takes place through carbon dioxide. This process provides energy to living organisms.
In turn, the organisms heterotrophs are the ones that capture organic matter from the environment, that is, they are not able to produce their food and carry out photosynthesis, feeding on other living beings, such as humans, fungi and bacteria.
Breathing
In relation to breathing, organisms can be anaerobic or aerobic. the organisms anaerobes produce energy in the absence of molecular oxygen and the aerobics it's the organisms that use oxygen to get their energy.
Learn more about the meaning of autotrophs, heterotrophs, Photosynthesis and eukaryotic cell.

