Just like human beings, the plants they need energy to survive.
However, unlike us, the means by which they gain energy is not called food, but photosynthesis, obtained by a process that uses the sun.
What is photosynthesis?
THE photosynthesis it is the method employed by autotrophic beings, those capable of producing their own food, detain the substances necessary for their survival.
As we've already mentioned, unlike humans and animals alike, the plants make up your food, converting the solar energy in organic matter.
Biologically speaking, this is triggered by the processing of carbon dioxide (CO2), water and minerals into organic compounds, releasing oxygen and water.
In summary, the photosynthesis equation can be simplified as follows:
6H2O + 6CO2 → LIGHT → 6O2 + C6H12O6
As it happens?
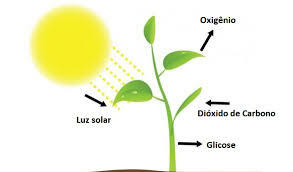 Photosynthesis takes place when water and mineral salts are extracted from the ground, through the roots of the plants, and pass from the stem to the leaves in the form of sap, the so-called raw sap.
Photosynthesis takes place when water and mineral salts are extracted from the ground, through the roots of the plants, and pass from the stem to the leaves in the form of sap, the so-called raw sap.
In this, the leaf absorbs sunlight with
chlorophyll, substance responsible for assigning the green color to the leaves of plants.Thus, chlorophyll together with solar energy, when faced with a photochemical reaction, and in the process of glucose formation, transforms solar energy into chemical energy.
In this way, the substance reached is carried through the existing channels to the different parts of the vegetable.
The plant feeds on part of this material to stay alive as well as keep growing.
The other properties are concentrated in the seeds, stem and root, in the form of starch.
What is the photosynthesis process and steps?
O photosynthesis process It is divided into two steps: light reaction (light phase) and carbon fixation reaction (dark phase).
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
light phase
Also known as the luminous phase or photochemical phase, it is one of the phases that can only be carried out in the presence of light, in the lamellae of the thylakoids of the chloroplast.
At this stage, there are two types of photosystems (photosystem I and photosystem II), with an average of 300 chlorophyll molecules.
In photosystem I, pairs of electrons pass through the P700 reaction center and preferentially absorb light at a wavelength of 700nm. In photosystem II, the P680 reaction center reaches light with a wavelength of 680nm.
Two important processes also take place here, photophosphorylation and photolysis of water.
dark phase
In the dark phase, the formation of glucose takes place from CO2, and this does not depend on the presence or absence of light.
The Calvin Cycle fixes the CO2 and it reduces the new fixed carbon, breaking the molecules and, showing a gain of one PGAL molecule, serving for the production of starch and sucrose.
Chemosynthesis
Chemosynthesis it is a procedure totally different from photosynthesis, by which it does not use solar energy and produces only the necessary organic matter to feed the organisms that carry it out.
Most often carried out by bacteria and archaebacteria, instead of solar energy, energy released by the oxidation of certain inorganic molecules is used.
Among them are sulfur (S), iron (Fe), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N) or manganese (Mg).
Photosynthesis and the environment
Extremely important for multiple forms of life on Earth, photosynthesis plays another very important role – that of cleaning the air.
Considering that, in their process, there is the elimination of carbon dioxide from the air, autotrophic beings contribute to nature in the purification of the air.
However, when producing glucose, vegetables eliminate oxygen, which is necessary for the planet's survival.
You might like this:
- Vegetative Organs in Plants: Roots
- Aquatic plants - What are they, names, types, examples, images
- All about succulent plants - What they are, how to care and examples
The password has been sent to your email.



