At glands of the human body are bodies that understand the systems endocrine and exocrine. The main function of the glands is to synthesize hormones, regulate and balance the metabolism of the body.
How they work to promote the functioning of various body organs, glands can be found in different locations.
The glands in the human body can be divided into endocrine and exocrine. In the endocrine system are found the thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary, pancreas, adrenals and sex glands.
The exocrine system is composed of salivary, sweat, lacrimal, mammary and sebaceous glands.
Index
- Glands of the endocrine system
- Mind Map of the Endocrine System
- Glands of the exocrine system
Glands of the endocrine system
At glands of the endocrine system they are responsible for the production of hormones that are released into the bloodstream to travel through the body and reach target organs.
Thyroid
THE thyroid it is located in the neck and acts in the production of T3 and T4 hormones that act in the regulation of metabolism. It is one of the largest glands in the human body.
Thyroid dysfunction can cause an increase or deficiency in the production of thyroid hormones, causing, respectively, hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
parathyroids
At parathyroids they are the four smallest glands in the body, are located around the thyroid and synthesize the hormone parathyroid hormone.
This hormone's main function is to regulate the amount of calcium in the individual's blood.
Hypophysis
THE hypophysis it is located in the middle of the head, is the size of a pea and has a lot of important information for the body.
It is the gland that controls the functions of other glands, coordinates the functioning of metabolism, and produces the ADH and growth hormones.
adrenals
At adrenals they are located above the kidneys, one on each side. They can also be called adrenal glands and have a triangular shape.
These glands act to release hormones such as adrenaline, cortisol, aldosterone and catecholamine. All of these hormones are involved in the body's metabolic and neurotransmitter processes.
sex glands
The sex glands can also be called the gonads, they are responsible for the production of gametes and sex hormones.
In men, the sex glands are the testicles that produce the sperm and synthesize testosterone.
The sex glands of women are the ovaries, they produce the secondary oocytes and synthesize estrogen and progesterone that regulate the menstrual cycle of the women.
pancreas
O pancreas it is a mixed gland, as it is part of both the endocrine and exocrine systems. In the endocrine system it produces hormones insulin, glucagon and somatostatin.
In the exocrine system, it is responsible for the synthesis of pancreatic juice, used during the digestion of the food we eat.
Mind Map of the Endocrine System

Click here to save this mind map in PDF!
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
Glands of the exocrine system
At exocrine glands they produce secretions or substances that are excreted in other organs or out of the body through channels.
Unlike hormones in the endocrine glands, these substances are not released into the bloodstream.
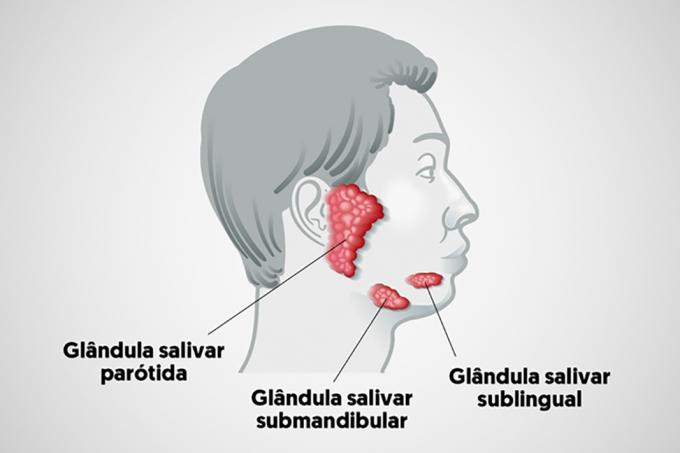
Salivary glands
At salivary glands are located in the mouth and throat, they cover the parotid, submandibular and sublingual regions.
The main function of these glands is to produce and release saliva that contains enzyme ptialin, responsible for the beginning of digestion in the mouth.
mammary glands
Mammary glands are unique to animals mammals, being present in both females and males.
However, only the female mammary glands develop and generate milk after the offspring are born.
The main function of the mammary glands is to produce milk to feed newborns.

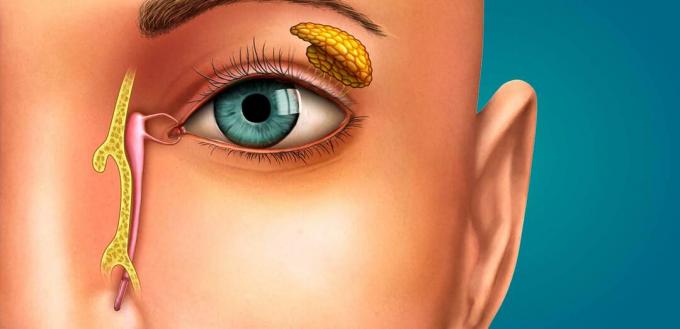
tear glands
The tear glands are located in the eyes and their main function is to lubricate the eyes and produce tears.
sebaceous glands
At sebaceous glands they are distributed throughout the body and they have the function of protecting, lubricating and moisturizing the skin.
These glands release fat, popularly called sebum. The regions with the greatest oil secretion are on the face and scalp.
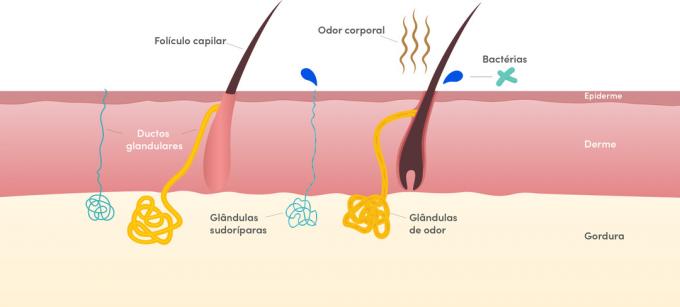
sweat glands
At sweat glands they are also spread throughout the body and their main function is to regulate body temperature.
These glands release water as well as toxic substances in the superficial region of the body. These glands can be divided into two types:
- Apocrine: they are glands that release odors, are in the armpit and genital region.
- Eccrine: they are glands spread throughout the body, their function is to maintain a constant body temperature.
Liver
O liver is the largest gland in the human body, it also acts in a mixed way between the endocrine and exocrine systems.
It has several functions, including: storing substances, synthesizing bile, cholesterol and some hormones.

See too:
- Acute appendicitis
- Ovulation and the fertile period
- Blood plasma
The password has been sent to your email.



