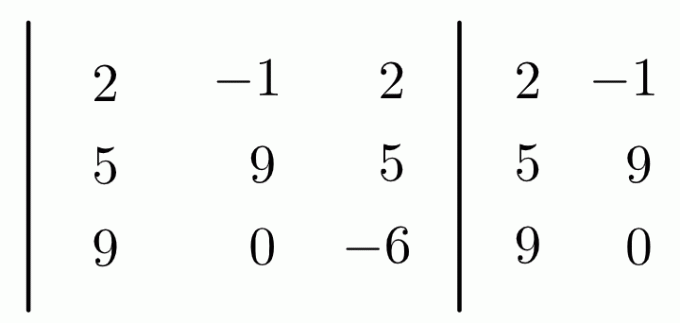With an area of approximately 880 km², the Paraná Hydrographic Basin covers seven states, in three different regions: São Paulo, Paraná, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Goiás, Santa Catarina and Distrito Federal. The population of about 61.3 million inhabitants, according to the 2010 census of the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), makes it one of the hydrographic regions with the highest population density in the parents.
The high number of inhabitants is reflected in the region's water demand, one of the largest in the country. Most of the resources are destined to agricultural irrigation, industrial activities and urban supply – together, the three correspond to 94% of the total demand.
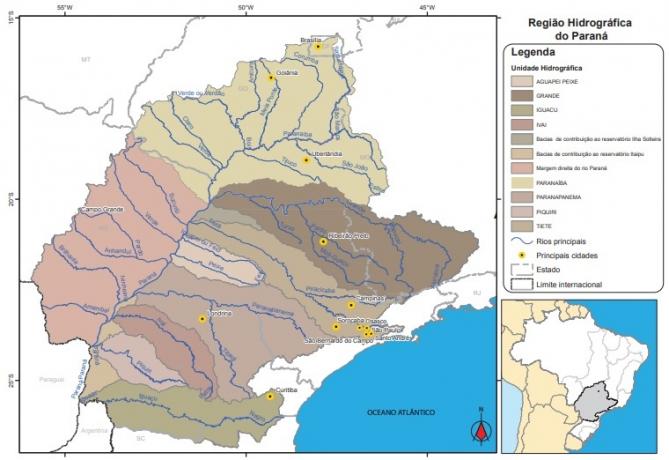
THE economic importance of the region is related to these activities, with the presence of large administrative and industrial centers in the country such as São Paulo, Santo André, São Bernardo do Campo, Sorocaba, Campinas, Curitiba, Londrina, Ribeirão Preto, Uberlândia, Goiânia and Brasilia.
The hydroelectric potential of the Paraná Basin, which also influences the economic issue, is large – around 41,560 megawatts. Important plants are located in the region, such as Itaipu, located on the Paraná River on the border of Brazil and Paraguay, and Furnas, built on the Rio Grande, in Minas Gerais.
In the region, the Paraná Waterway is also located, with 1,800 km in length. Result of the channeling of the Tietê and Paraná rivers, it also comprises the forming rivers, Grande and Paranaíba, in addition to some tributaries.
Index
- critical issues
- Main data
- Sub-divisions
- Main Rivers
- Hydroelectric Power Plants
critical issues
The water quality of the Paraná basin, especially in urban regions, is more compromised. This happens through the dumping and not treatment or total collection of all the sewage. Data from the Ministry of Cities in 2012 show that most of the urban population in the region has access to water supply (98.5%) and sewage collection (70.6%).
In addition to water pollution, at certain points, the springs were degraded or underwent an intense process of occupation, which also impacts the region's nature.
The use for irrigation in certain regions of the basin has very high demands. In Paranapanema, for example, 90% of the Alta Paranapanema's water demand is destined to irrigate the region's plantations.
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
At certain points, the region is also vulnerable to flooding, due to erosion or flood problems.
Main data
Total area: 879,873 km² (10% of the Brazilian territory)
Population (2010 Census): 61.290.272
Location: São Paulo, Paraná, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Goiás, Santa Catarina and the Federal District
Number of municipalities: 1.507
Demographic density: 69.7 inhab./km²
Water availability: 5,956 m³/s
Sub-divisions
- Aguapeí Fish
- Great
- Iguazu
- ivai
- Paranaíba
- Paranapanema
- piquiri
- tiete
- Contribution basins to the Itaipu reservoir
- Tributaries of the right bank of the Paraná River
Main Rivers
- Parana River
- big River
- Iguazu River
- Paranaíba River
- Tiete river
- Paranapanema River
- Ivaí River
- Tibagi River
- Rio Pardo
- Amambaí River
- Aporé River
- green River
- Golden River
- Sucuriú River
Hydroelectric Power Plants
- Itaipu Hydroelectric Power Plant (Paraná River, Mato Grosso do Sul)
- Ilha Solteira Hydroelectric Power Plant (Paraná River, border between São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul)
- Itumbiara Hydroelectric Power Plant (Rio Paranaíba, border between Goiás and Minas Gerais)
- Engenheiro Sérgio Motta Hydroelectric Power Plant (Porto Primavera) (Paraná River, border between São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul)
- Marimbondo Hydroelectric Power Plant (Rio Grande, border between São Paulo and Minas Gerais)
- Salto Santiago Hydroelectric Power Plant (Rio Iguaçu, Paraná)
- Furnas Hydroelectric Power Plant (Rio Grande, Minas Gerais)
- Engenheiro Souza Dias Hydroelectric Power Plant (Jupiá) (Paraná River, border between São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul)

Subtitle:
CGH - Electric Generating Center
SHP – Small Hydroelectric Power Plant
HPP – Large Hydroelectric Power Plant
HR - Hydrographic Region
The password has been sent to your email.