Life in large urban centers often distances us from the variety of animal species that exist on our planet. A few years ago it was estimated that the Animalia Kingdom would have between 2 to 8 million species, which would already be an extremely significant number. However, today studies indicate that this number exceeds 50 million and among these species, science knows just over 1.5 million. It is worth remembering that we will hardly know all the species someday, anthropogenic interference causes many species to become extinct even before they are discovered by science.
The members of the Animalia Kingdom are studied according to their characteristics within Zoology. We can divide these individuals into invertebrates, a group that contains eight main phyla, and chordate, which can be divided into subphyla. protochord and vertebrates.
Index
- Invertebrates
- Strings
- Symmetry and locomotion in the Animalia Kingdom
Invertebrates
The invertebrate group is very diverse and its main characteristic is the absence of a backbone. These individuals also have: multicellular formation; are eukaryotes; with the exception of sponges, they have tissue organization, that is, cells organized to form tissues; are aerobic (take oxygen from the air or water); it has bilateral symmetry, that is, two equal halves of the body; and its mode of reproduction is generally sexual (with gamete switching). They usually have a soft body, but in some groups such as arthropods, these animals have a limestone exoskeleton that is intended to assist in the support, locomotion and protection of this animal.
Most of these individuals are able to move around, but sponges only manage to do so when they are still very young, in adulthood they are sessile. Invertebrates need other living beings to obtain energy through food, or that is, they are heterotrophs and can feed on both autotrophic and other individuals. heterotrophs.
The main phyla of invertebrate animals are: arthropods, molluscs, coelenterate, poriferous, echinoderms, flatworms and annelids. Examples of animals from these groups are: spiders, centipedes, centipedes, octopuses, starfish, worms, insects (flies, mosquitoes, cockroaches, beetles, butterflies, etc.), sea sponges, shellfish, among others. Invertebrates can be terrestrial, aquatic or parasites of the human body and other animals.

- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Preschool Math Games Course
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
Strings
the individuals of Chordata phylum or Filo Cordados have as a common characteristic the presence of the notochord at some stage of their lives, this indicates the existence of a common ancestor for these individuals. The notochord is located between the neural tube and the digestive tube in a dorsal and longitudinal position, it is the first supporting structure of a chordate body and is shaped like a massive rod and flexible. In some animals the notochord remains in the adult stage as in protochords, whereas in other animals it is replaced by the vertebral column, as in the case of humans. These animals have three germinative leaflets, that is, they are triblastic, they are deuterostomies, that is, the blastopore (structure similar to a mouth) gives rise to the anus, and they are coelomic animals.
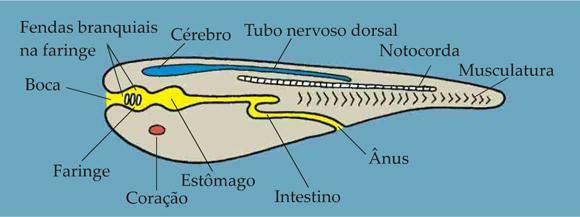
The chordates have other embryonic structures, in addition to the notochord, which may or may not disappear in the adult stage of the individual. One of these structures are the gill clefts in the pharynx, in individuals with aquatic habits these gill clefts remain in the adult stage and assume a respiratory function. In terrestrial chordate, these structures disappear so that the trachea can appear in the pharynx, which is the structure with respiratory function in these animals.
This group is also characterized by the presence of a dorsal nervous system that is located above the notochord. This dorsal nervous system originates from the embryo's dorsal ectoderm and is well developed in individuals. adults, with the exception of some protochordates that even in adulthood do not have the dorsal nervous tube well. developed. The nervous system of non-chordate animals is much simpler, occupies a ventral position and can be of the ganglionic type.
Symmetry and locomotion in the Animalia Kingdom
In the Animalia Kingdom we can find very simple animals that have irregular shapes and are called asymmetrical, such as sponges, even animals with much more complex morphology and symmetries full of particularities, such as beings humans. In these complex individuals, we can trace vertical planes of symmetry that allow for the separation of the animal into halves. isomorphic, we say that these animals are radially symmetrical, in general this occurs in cylindrical or shaped animals. bell. Radial symmetric animals usually have life habits fixed to the substrate (cnidarian polyps or adult sponges) or move slowly (jellyfish, starfish, etc.).
Even with the presence of asymmetric animals and radial symmetry, the type of symmetry that really predominates in the Animalia Kingdom is bilateral. In these animals, there is the presence of a left and right side, ventral and dorsal sides, and extremities anterior (where the head is located) and posterior (mostly housing the anus and orifices breeders). In the bilateral symmetry model, there is only one sagittal plane that splits the animal into two equivalent halves. Many animals with this type of symmetry act in the ecosystem as predators, it is believed that this symmetry is related to the way of life of these individuals.
Denisele Neuza Aline Flores Borges
Biologist and Master in Botany
The password has been sent to your email.

