THE embryology it is the science that studies all stages of embryonic development of living beings after fertilization, at which time two gametes are united forming the zygote, which will give rise to the new individual.
However, embryology also studies the stages that precede the embryo's gestation, as they influence the development process.
Embryology is part of Developmental Biology and relates to different areas such as cytology, a histology, a genetics, a zoology, a botany, etc.
Embryology can be studied in different areas, for example, human embryology, which isstudy the human embryo development, malformations and congenital diseases that may occur.
We also have the andcomparative embryology, which studies the embryonic development of many species of animals. This area is very important for the evolutionary processes to be clarified.
And another example is plant embryology, which studies all stages of embryonic development for the formation of new plants.
Index
- Egg or zygote cell types
- human embryology
- Fetal develop
Egg or zygote cell types
In embryology, the word egg has a broad biological meaning and can be used to designate the zygote, which is the result of fertilization.
In animals, the egg cell, in addition to carrying genetic information, also has nutritional reserves called the calf, whose distribution depends on the species in which it is found.
US vertebrates, the calf is synthesized in the mother's liver and is taken through the blood to the ovaries to deposit in the female gamete.
Egg types can be classified according to the amount and distribution of the yolk within the cell.
Oligolet or isolocyte eggs
Oligoletic eggs have a small amount of yolk that is evenly distributed throughout the cytoplasm. They are present in:
- porifers: sponges
- Cnidarians: anemone and jellyfish
- echinoderms: starfish
- roundworms: worms
- Protocols: amphioxus
- Mammals: all except the platypus
In placental mammals, such as humans, the oligolectic egg develops within the mother's body and receives protection and nutrition through the placenta.
heterolecite or mesolocyte eggs
Heterolecitos eggs have a reasonable amount of yolk, intermediate the amount of other types of eggs. This calf is not evenly distributed, it is located only on one side, called the vegetative pole, and on the other side is the cell nucleus.
They are present in:
- platyhelminths: tapeworm and schistosome
- annelids: worm
- molluscs: slug, snail
- amphibians: frog Toad
In amphibians, the egg cell develops and forms a larva, called a tadpole, which removes other food supplements from the aquatic environment.
eggs telolocytes or megalocytes
The telolocyte eggs have a large amount of yolk that is concentrated in the vegetative pole that occupies almost the entire cytoplasm of the cell, leaving the nucleus in the periphery of the cell.
This type of egg can be found at:
- Cephalopod molluscs: octopus and squid
- Fish
- reptiles
- birds
- Monotreme mammals: platypus, echidna
Embryos that arise from this type of egg develop outside the female's body. Some get limestone husks inside the mother's body for protection, as in chicken eggs.
Centrolecitos eggs
Centrolecitos eggs have a similar amount of yolk to mediolecites eggs, however, the distribution is different. The calf is concentrated around the core.
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
This type of egg is found in arthropods like insects, crustaceans and arachnids.
human embryology
Human embryonic development has many stages, let's get to know each one in more detail.
Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is the process of formation of gametes from germ cells that go through successive mitotic divisions and multiply.
These germ cells grow and pass through the meiosis I and form daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes of the starting cell.
In female gametes, meiosis does not happen completely and gives rise to a secondary oocyte and a smaller primary polar body. Meiosis of female gametes is complete only if the released egg is fertilized.
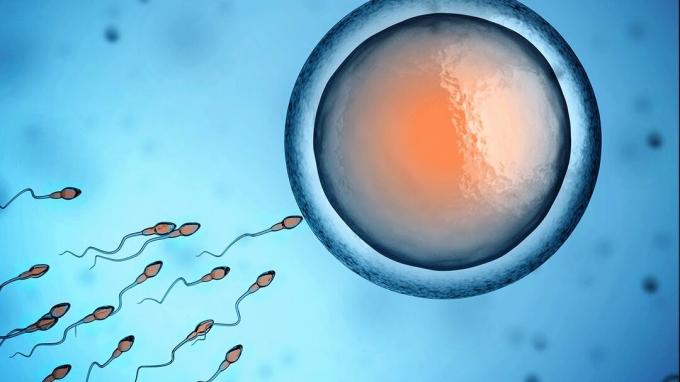
Fertilization
Human fertilization occurs during sexual intercourse when sperm are released into the female body and encounter the oocyte.
The meiotic division of the oocyte ends up taking place when the sperm enters it, and thus fertilization takes place.
Therefore, fertilization is the fusion of two haploid gametes that give rise to a diploid cell called a zygote or egg cell.
Fetal develop
The development of zygotes that were formed during fertilization occurs in three stages: segmentation, gastrulation and organogenesis.
Segmentation
The segmentation of the zygote starts with the cleavages, that is, the divisions that cause the number of cells to increase. This step takes place in approximately one week when the zygote is in the blastocyst stage and will still attach to the uterine wall.
Gastrulation
In the gastrulation phase, in addition to the number of cells, the embryo's volume also increases. In this step, three embryonic leaflets: the ectoderm, the mesoderm and the endoderm.
The development of these embryonic leaflets initiates cell differentiation that will originate tissues and organs throughout the body.
Organogenesis
Organogenesis corresponds to the organization of tissues in organs. The organs of nervous system they are the first to be formed, they originate from the ectoderm, the outermost embryonic leaflet.
The formation of the nervous system takes place around the third week of embryonic development, that is, after fertilization.

Mind Map — Embryology
Take the opportunity to paste the map in your notebook and study whenever necessary!

Click here to download this mind map in PDF!
See too:
- sexual reproduction
- Natural selection
- The 13 systems of the human body
- How many bones are there in the human body?
- What is the smallest bone in the human body?
The password has been sent to your email.

