Youchromosomesthey are structures formed by a DNA molecule associated with protein molecules. In the cells prokaryotes, we observe a circular chromosome; US eukaryotes, you chromosomes are linear and are located inside the nucleus.. In this text we will talk about the chromosomes present in eukaryotes.
→ Chromosome structure
Chromosomes, as already said, are formed by DNA and associated proteins, a complex called chromatin. Associated proteins help to fold the DNA molecule, reducing its length. In chromatin, we observe the presence, mainly, of proteins called histones.
When the cell enters cell division, we see changes in the structure of the chromatin, which becomes highly compacted, forming what we call a chromosomes. at the stage of metaphase, the period of greatest condensation is observed, being possible to better count and analyze the chromosomes.
→ Chromosome Parts
When we look at a chromosome in metaphase, it is possible to observe important structures:
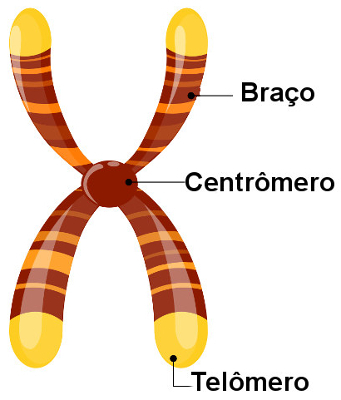
Look at the main parts of the chromosome
-
Centromere: regions of primary constriction of the chromosome. In this place, the kinetochore is located, a structure formed by proteins that guarantee the connection of the sister chromatids (each copy of the duplicated chromosome) in the mitotic spindle. The centromere makes it possible to divide the chromosome into arms, which can have different sizes depending on the position of the centromere. When we look at an unduplicated chromosome, it is possible to notice the presence of a centromere and two arms.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The position of the centromere allows you to classify it into metacentric (centromere in the median position), submetacentric (centromere displaced to one of the arms of the chromosome), acrocentric (centromere located closer to the end) and telocentric (the centromere is located very close to the end, giving the idea that the chromosome has only one arm);
Telomeres: regions found at the ends of chromosomes. There are no genes in them, only small nucleotide repeats are found. The function of telomeres is to ensure protection.
→ Number of chromosomes of a species
Each species has a specific number of chromosomes. In a human somatic cell, we observe the presence of 46 chromosomes; in the sex cells, there are only 23 chromosomes. This reduction in sex cells is important to reestablish the number of chromosomes of the species after the fertilization process.
We say that the somatic cells are diploidsbecause they have two sets of chromosomes, the chromosomes being, therefore, in pairs. The similar chromosomes that form each of these pairs are called counterparts. In the sex cells, there are no homologues, just a group of chromosomes. These cells, therefore, are haploids.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "What is a chromosome?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/biologia/o-que-e-cromossomo.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.