A gas is characterized by three properties, called state variables, which are: pressure, volume and temperature. When one or more of these variables changes, a gas transformation, which can be classified as isothermal, isovolumetric or isobaric.
is called isothermal transformation the gas transformation in which the system temperature remains constant, variations occurring only in the pressure and in the volume of gas.
This transformation is also calledBoyle-Mariotte's Law — name given in honor of Boyle, an Irish chemist who, in 1660, passed a law stating that, in a given sample of ideal gas, the product of the pressure and the volume occupied by the gas is constant when the temperature does not vary, and also in honor of Mariotte, a French physicist who, in 1676, independently discovered the same law.
In summary, the law that describes the behavior of a gas during an isothermal transformation can be stated as follows:
“In isothermal transformation, the pressure exerted by an ideal gas sample is inversely proportional to its volume change.”
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
From this law, we can conclude that, when increasing the pressure of a gas mass, there will be a decrease in the volume occupied by it and vice versa. Therefore, the product between these two quantities will remain constant.
Mathematically, Boyle-Mariotte's Law can be described by the expression:
P. v = constant
As the product between pressure and volume is constant, we can conclude that:
P1. V1 =p2 . V2
In addition, this law is also graphically represented:
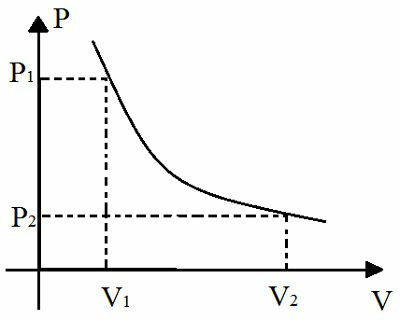
This graph represents the relationship between pressure change and temperature change during an isothermal transformation
The graphical representation of the isothermal transformation is a hyperbola. The larger the product p. V of this transformation, the further away this hyperbola will be from the axes of the graph. The name given to this curve represented in the graph is isotherm.
By Mariane Mendes
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
TEIXEIRA, Mariane Mendes. "What is isothermal transformation?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-transformacao-isotermica.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.