At covalent bonds, also called molecular or homopolar bonds, are those that occur between atoms of electronegative elements, that is, with a tendency to receive electrons, establishing a bond of sharing electrons from their valence shells.
Covalent bonding can occur between the following elements: hydrogen, non-metals and semi-metals. Metals never participate in this type of bonding.
Let's consider a simple example of a covalent bond: the hydrogen gas-forming bond (H2):
H + H → H2
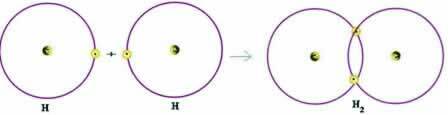
Note that both atoms needed to receive an electron to complete their valence shell – according to the Octet Rule – and, in this way, to remain stable. Therefore, they shared their electrons and, in this way, they both had two electrons, had their complete K-shell and acquired configuration of the noble gas helium.
This sharing of electrons is what differentiates this type of bond from ionic bonding, in which electron transfer takes place.
See the figure below for two more examples of this case:
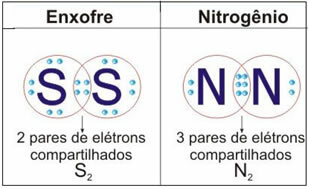
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
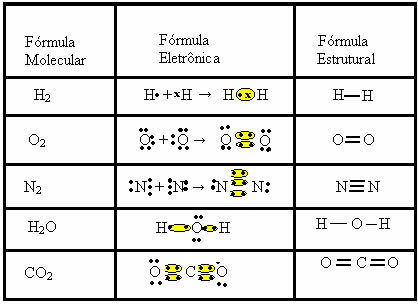
In this type of bond there is the formation of molecules, which can be represented by their respective molecular formulas, that is, the simplest representation that indicates how many atoms of each element there are in the molecule. Some examples of molecular formulas are: H2, S2, O2, no2, H2O, CO2, etc.
The covalent bond can be represented by two other formulas:
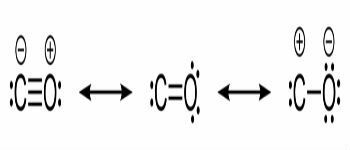
- Electronic Formula or Lewis Formula: in this formula also appear the electrons of the valence shell of each atom and the formation of electronic pairs. These electrons are symbolized by the signs . or x;
- Flat Structural Formula or Couper Structural Formula: shows the links of the elements, with each shared pair corresponding to a dash. If it's just a dash we call it a single link; if there are two, double bond; and if there are three dashes, triple bond.
Look at other examples of covalent bonds being represented by these three chemical formulas:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Covalent Bonds"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/ligacoes-covalentes.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.