Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, ions or molecules.
In an oxidation-reduction reaction, changes in the oxidation number (nox) occur. Oxidation consists of the oxidation and reduction processes:
- Oxidation: results in electron loss and increased nox.
- Reduction: results in electron gain and decreased nox.
As one element gives up electrons, another will receive them. Thus, the total number of electrons received is equal to the total number of electrons lost.
Examples of redox reactions to combustion, corrosion and photosynthesis.
Examples
Depending on the element that receives or donates electrons, we have the following names:
- Reducing Agent: One that undergoes oxidation causes reduction and increases its nox number. It's what loses electrons.
- Oxidizing Agent: The one that undergoes reduction, causes oxidation and decreased its nox number. It's what gains electrons.
O oxidation number represents the electrical charge of an element at the time it participates in a chemical bond.
This condition is related to the electronegativity, which is the tendency of some elements to receive electrons.
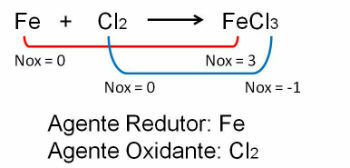
1. Observe the first example, note that in the reaction between Iron and Chlorine there is a change in the oxidation number. O chlorine because it is more electronegative it gains electrons:
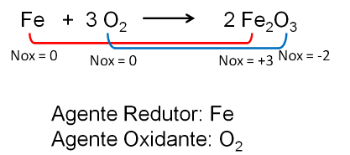
2. Reaction between Iron and Oxygen. Oxygen is more electronegative and ends up receiving electrons and decreasing their oxidation number.
Learn more, read also:
- Oxidation
- Combustion
- Chemical reactions
- electrons
Exercise solved
1. (PUC-RS) In relation to the oxidation equation - unbalanced reduction Fe0 + CuSO4 → Fe2(ONLY4)3 + Cu0, it can be said that the:
a) oxidation number of copper in cupric sulfate is +1.
b) iron atom loses 2 electrons.
c) copper undergoes oxidation.
d) iron is an oxidizing agent.
e) iron undergoes oxidation.
Resolution:
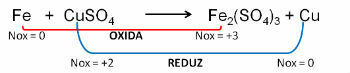
Reply:
e) iron undergoes oxidation.
Exercises
1. (UFAC-AC) In the following chemical equation: Zn + 2 HCℓ → ZnCℓ2 + H2
a) the element Zn oxidizes and reacts as an oxidizing agent.
b) the Zn element oxidizes and reacts as a reducing agent.
c) the Zn element reduces and reacts as a reducing agent.
d) HCℓ is a reducing agent.
e) the equation is classified as reversible.
b) the Zn element oxidizes and reacts as a reducing agent.
2. (ITA-SP) In the ionic reaction Ni(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Ni2+(aq) + Cu (s)
a) nickel is the oxidizer because it is oxidized.
b) nickel is the reducer because it is oxidized.
c) the cupric ion is the oxidizer because it is oxidized.
d) the cupric ion is the reducer because it is reduced.
e) it is not a redox reaction, therefore there is no oxidant or reducer.
b) nickel is the reducer because it is oxidized.
3. (UFRGS) The active agent in household bleach is the hypochlorite ion, ClO-. In bleaching processes, this ion is reduced; This means that:
a) the substance that undergoes the action of hypochlorite receives electrons.
b) there is a decrease in the number of electrons in its structure.
c) ClO- is a reducing agent.
d) ClO- is converted to elemental chlorine or chloride ion.
e) no electron transfer takes place.
d) ClO- is converted to elemental chlorine or chloride ion.