O endocrine system is a complex system and constituted by the endocrine glands of our body. Endocrine glands are the structures that synthesize substances and release them into the bloodstream. These substances are called hormonesand are responsible for controlling a number of activities in the human body, such as metabolism, milk secretion, growth and the amount of calcium in the blood. It is important to point out, however, that endocrine cells can be found in organs that make up other systems, such as the hormone-producing cells found in the stomach.
Read too: Human body: body parts and their functions
endocrine glands
At glands they are structures responsible for the secretion of substances. We can classify the glands into endocrine, exocrine and mixed. Atendocrine glandsthey release their secretions, called hormones, into the blood, where they are transported until they reach their place of action. These are the glands we look at when studying the endocrine system. The exocrine glands, in turn, have ducts that ensure that their secretion is released into cavities or on body surfaces. Finally, we have the mixed glands, which have endocrine and exocrine portions.
Hormones
You hormones are signaling molecules that act in specific places of the body. They circulate through the body through the bloodstream and bind to specific receptors. Therefore, even if a hormone circulates throughout the body, it will only have its action performed when it reaches the cell that has receptors for that given hormone.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Some hormones act on various cells present in the body, such as thyroxine, produced by the thyroid, which ensures the increase in the speed of chemical reactions in almost every cell in the body. Other hormones, however, act on target tissues, such as the adrenocorticotropic hormone, produced by the pituitary, which stimulates the adrenal cortex.
Hormones are essential for the functioning of the human body, acting on practically all the activities of our body. Reproduction, growth and even metabolism are some of the activities that have hormonal regulation.
Read too: Oxytocin: the love hormone?
Main glands that form the endocrine system

See the table below with the main endocrine glands in the human body and the hormones they produce:
endocrine gland |
Hormones and some of their functions |
Pineal gland |
melatonin: acts in the regulation of biological rhythms. |
Hypothalamus |
Inhibition and release hormones: The hypothalamus produces several hormones that stimulate the pituitary to secrete other hormones. Oxytocin*: stimulates the contraction of the uterus and the ejection of milk by the mammary glands. Vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone (ADH)*: acts on the reabsorption of water by the kidneys. *Hormones produced by the hypothalamus and released by the neurohypophysis. |
Hypophysis |
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): acts on the female and male gonads, promoting the growth of ovarian follicles and sperm maturation. Luteinizing hormone (LH): acts on the female and male gonads, acting to stimulate ovulation and testosterone synthesis. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH): stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete its hormones. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): stimulates the adrenal cortex. Prolactin: stimulates milk secretion. Growth hormone (GH): stimulates growth. |
Thyroid |
Thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3):they act on metabolic processes. Calcitonin: reduces blood calcium levels. |
parathyroids |
parathormone: Increases blood calcium levels. |
adrenals |
epinephrine and norepinephrine: produced in the adrenal medulla, have the same effects as sympathetic stimulation, promoting, for example, vasoconstriction and increasing blood glucose level. Glucocorticoids: produced in the adrenal cortex, it plays a role in glucose metabolism. Mineralocorticoids: produced in the adrenal cortex, it acts on sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in the kidneys. |
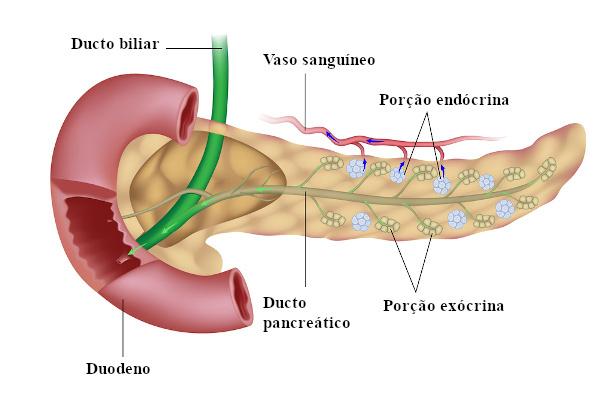
pancreas |
Insulin: works by reducing blood glucose levels, promoting the entry of glucose into cells. Glucagon:it works by increasing blood glucose levels. |
ovaries |
estrogen:participates in the menstrual cycle and development of female sexual characteristics. Progesterone: promotes endometrial growth during the menstrual cycle. |
Testicles |
Testosterone: promotes the development of the male reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. |
It is noteworthy that, in addition to the endocrine glands, we have some organs that act in a secondary way as endocrine organs. This is because these organs have the ability to produce hormones, but that is not their main function. Endocrine cells and tissues are seen, for example, in the stomach, liver, heart, thymus, kidneys and small intestine.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Endocrine system"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/sistema-endocrinico.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.

