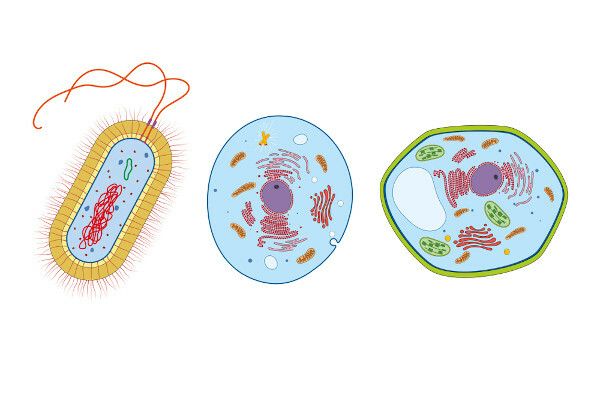
O cytoplasm is a localized region, in the eukaryotic cells, between the plasma membrane and the nuclear membrane. In the prokaryotic cells, as they do not have a nucleus, the cytoplasm corresponds to the internal region of the cell. It is in the cytoplasm that we find cell structures called organelles as well as the cytoskeleton and lipid inclusions and glycogen granules. The space between the organelles is called the cytoplasmic matrix or cytosol.
Read too: Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
The cytoplasm in eukaryotes
The cytoplasm corresponds to all cell content located outside the core. It contains a varied amount of membranous organelles,which perform the most varied functions. The part of the cytoplasm located between the organelles is called cytosol or cytoplasmic matrix, in which important chemical reactions happen.
The cytosol has a consistency that varies between a sun and a gel. This consistency is acquired thanks to its composition, which includes a large amount of large and small molecules. Formed mainly by water, the cytosol also has other substances such as
proteins, amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids and ions.It is worth noting that the cytoplasm does not behave just like a soup containing compounds and organelles. When we look under an electron microscope, the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell is crossed by a series of filaments, which form a sort of network.
This network is called cytoskeleton, which consists of actin filaments, microtubules and intermediate filaments. These three types of filaments provide mechanical reinforcement to the cell, help in the movement and process of cell division. Furthermore, the cytoskeleton is important to ensure proper placement of the organelles.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Cell organelles
At cell organelles are suspended in the cytosol and are found in eukaryotic cells. It is noteworthy that the ribosomes, as they do not have membranes, they are not considered cell organelles by some authors. Others, however, call it non-membranous organelles. Regardless of classification, ribosomes are complexes made up of ribosomal RNA and proteins, whose function is protein synthesis. These structures are present in both the cytosol of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
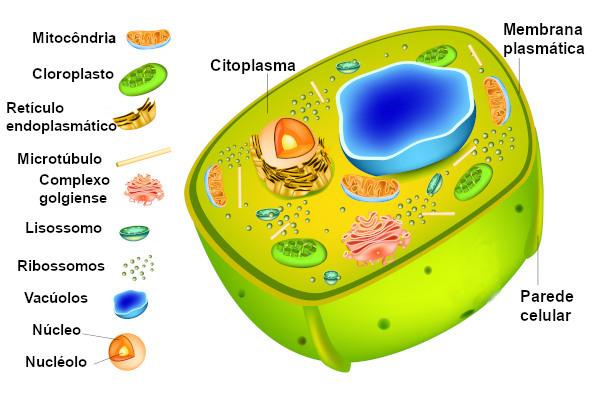
See below the names of some cell organelles and some of the functions they perform:
Cell organelles | |
Organelles |
Occupation |
mitochondria |
Responsible for cellular respiration. |
Lysosome |
Organelle related to intracellular digestion. |
Chloroplast (exclusive of the plant cell) |
Photosynthesis site. |
endoplasmic reticulum smooth |
Involved in different processes such as lipid synthesis and detoxification. |
Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
Involved in processes such as protein production. |
Golgi complex |
Related to cell secretion. |
vacuole central or cellular juice vacuole (exclusive to the plant cell) |
They act, for example, in the accumulation of substances and maintenance of the cell's pH. |
Read too: Differences between animal and plant cells
cytoplasmic movements
As we have seen, the cytoskeleton is related to the movement of the cytoplasm. Two cell movements can be identified: amoeboid movement and cyclosis.
- Amoeboid movement: leads to the displacement of the entire cell. In this case, there is the appearance of cytoplasmic projections, called pseudopods, which arise due to the interaction between actin and myosin filaments that promote cell contraction.
- Cyclosis: it consists of a circular cytoplasmic stream, in which it is possible to observe organelles and various substances moving in an orderly manner. This current is important to guarantee the exchange of substances within the cell and also between the cell and the environment. It is also caused by interactions between actin and myosin.
Read too: Phagocytosis - better understand the importance of cytoplasmic movements
Cytoplasm Functions
The cytoplasm is fundamental for the cell, performing various functions, such as:
- It serves as a place to carry out different chemical reactions;
- Facilitates the exchange of substances within the cell and between adjacent cells;
- Due to the presence of the cytoskeleton, the cytoplasm acts promoting the support of the cell and guaranteeing its movement, in the case of the one that presents amoeboid movement.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Cytoplasm"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/o-citoplasma-das-celulas.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.

