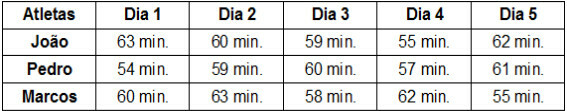
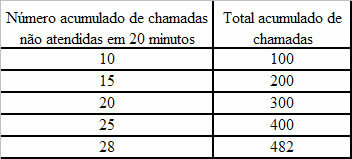
At Statistic studied in elementary and high schools, there are two types of measures used to analyze the information: the central tendency measures and the dispersion measures. At measuresintrendcentral are used to represent all the numbers in a list, such as the average student grade that represents all of a year's performance.
On the other hand, the measuresindispersal are applied to determine the degreeinvariation of numbers on a list with respect to your average. In a way, dispersion measures analyze the distance of numbers from a set to the average of that set. Are they: amplitude, Detour, variance and Detourstandard.
Use of measures of central tendency and dispersion
At measuresintrendcentral they are mode, average and median. THE fashion is the number that is most repeated in a set; The average is the number that is in the center of the set, if its elements are arranged in ascending or descending order. THE average is the sum of all the numbers in a list divided by the number of numbers that have been added.
Any of these three results have the same function, although they are different results used in different situations. Suppose two students have achieved the same average at school: 7.0. The grades of the first student were: 8.0; 7,0; 7.0 and 6.0. The second grades were 4.0; 5,0; 9.0 and 10.0. It will be possible to determine which of the two students had the greatest progress from their averages?
The answer is no! It is necessary to know all the grades of these students to discover that the first one regressed and the second one had an excellent development, even though both have achieved the same average. You can also determine this difference through the measurements used to find the degreeinvariation, in this case, from the students' grades.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
For this, the measuresindispersal: amplitude, Detour, variance and standard deviation. The definitions of variance and Detourstandard depend on the definition of offset, which will be discussed shortly thereafter. For more information on variance and standard deviation, Click here.
Amplitude
THE amplitude of a set, in Statistics, is the difference between the largest element of that set and the smallest. In other words, to find the span of a list of numbers, just subtract the smallest element from the largest.
In the example given above, there are two amplitudes to be evaluated: the first and the second student. The first student has 8 as the highest grade and 6 as the lowest. The range of his grades was: 8 – 6 = 2. The second student had 10 as his highest grade and 4 as his lowest. The range of his grades was 10 – 4 = 6. Although it is not possible to determine which of the two performed better by this measure alone - as it is not possible to know which of the two had an increase in grades - these results already say that the variation the first student's grade point was much lower than that of the second.
Detour
O Detour is the difference between one of the numbers in a set and the average of that set. Therefore, each of the numbers in a set has a deviation, and this result can be different for each of these elements.
Note, for example, the deviations of the first student's grades, knowing that his average was 7.0:
d1 = 8,0 – 7,0 = 1,0
d2 = 7,0 – 7,0 = 0,0
d3 = 7,0 – 7,0 = 0,0
d4 = 6,0 – 7,0 = – 1,0
By Luiz Paulo Moreira
Graduated in Mathematics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Luiz Paulo Moreira. "Dispersion measures: amplitude and deviation"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/medidas-dispersao-amplitude-desvio.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.