At units of measure they are representations of physical quantities used in different areas of knowledge in order to quantify a matter, a sensation, the time or the size of something, for example.
All over the world the measurement units follow a pattern determined by the International System of Units (SI). From the standard unit established by the International System, we can still use other units derived from it, which allows us to compare and expand the quantitative notion of quantity.
The International System adopts the kelvin unit, for example, as a standard for the quantity temperature. This unit is widely used in laboratory experiments, but in everyday life most countries use the degrees Celsius unit, which is derived from the kelvin unit.
Read too: Vector and scalar quantities
mass units
The most used units for working with the mass of a matter are:
Tonne (t);
Kilogram (kg) [standard unit of mass according to SI];
Gram (g);
Milligram (mg).
To convert one unit into another, just follow these relationships:
1 t = 1000 kg
1 kg = 1000 g
1 g = 1000 mg
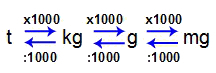
Relation between mass units
As we can see, one unit of mass is always 1000 times greater than the other. See some examples:
→ Conversion of mass units
Example 1: Let's transform 2.5 kg into grams.
Since 1 kg is equal to 1000 grams, we can set up the following rule of three:
1 kg 1000 g
2.5 kg x
x. 1 = 2,5.1000
x = 2500 g
Example 2: Let's transform 4 mg into kg.
As 1 kg is equivalent to 1000000 of mg (result of multiplying 1000 x1000 of the difference between the unit kg and mg), we can set up the following rule of three:
1 kg 1000000 mg
x 4 mg
1000000.x = 4.1
x = 4
10000000
x = 0.000004 kg
volume units
cubic meter (m3) [standard unit of volume according to SI];
Liter (L) or cubic decimeter (dm3);
Milliliter (mL) or cubic centimeter (cm3).
To convert one unit into another, just follow these relationships:
1 m3 = 1000 L
1L = 1 dm3
1L = 1000 mL
1dm3 = 1000 cm3
1cm3 = 1ml

Relationship between volume units
As we can see in the diagram above, one unit of volume is always 1000 times larger than the other. When we compare the larger unit (m3) with the smallest unit (mL or cm3), the difference is 1,000,000 times.
→ Conversion of volume units
Example 1: let's transform 4.5 m3 in dm3.
like 1 m3 equals 1000 dm3, we can set up the following rule of three:
1m3 1000 dm3
4.5 m3 x
x.1 = 4.5.1000
x = 4500 dm3
Example 2: let's transform 300 cm3 in L.
As 1 L equals 1000 cm3, we can set up the following rule of three:
1L 1000 cm3
x 300 cm3
1000.x = 300.1
x = 300
1000
x = 0.3 dm3
pressure units
The most used units for working with the pressure they are:
Atmosphere (atm);
Millimeter of mercury (mmHg);
Centimeter of mercury (cmHg);
Pascal (Pa) or kilopascal (KPa = 1000 Pa) [standard pressure unit according to SI].
To convert one unit into another, just follow these relationships:
1 atm = 101.325 kPa
1 atm = 101325 Pa
1 atm = 760 mmHg
1 atm = 76 cmHg
NOTE: Relationships starting from atm were used because the values used are numerically simpler to work and/or memorize (if necessary).
→ Conversion of pressure units
Example 1: Let's transform 2 atm into KPa.
As 1 atm is equivalent to 101,325 KPa, just set up the following rule of three:
1atm 101,325 KPa
2 atm x
x.1 = 2,101,325
x = 202, 650 KPa
Example 2: Let's transform 200 mmHg into cmHg.
Using the relationships given above, we must initially convert 200 mmHg to atm using the following rule of three:
1 atm 760 mmHg
x 200 mmHg
x.760 = 200.1
x = 200
760
x = 0.26 atm
We then transform the result in atm to cmHg in the following rule of three:
1 atm 76 cmHg
0.26 atm y
y.1 = 0.26.76
y = 19.76 cmHg
Example 3: Let's transform 500 cmHg into KPa.
Using the relationships given above, we must initially convert 500 cmHg to atm using the following rule of three:
1 atm 76 cmHg
x 500 cmHg
x.76 = 500.1
x = 500
76
x = 6.57 atm
We then transform the result in atm to cmHg in the following rule of three:
1 atm 101,325 KPa
6.57 atm y
y.1 = 6.57,101.325
y = 665.70 KPa
See too:What is atmospheric pressure?
temperature units
The most used units for working with temperature they are:
Degrees Celsius (OÇ);
degrees Fahrenheit (OF);
Kelvin (K) [standard temperature unit according to SI].
To convert one temperature unit into another, we can use the following formulas:
From degrees Celsius to Kelvin: TK = TOC + 273
From degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit: TOÇ = TOF-32
5 9
→ Conversion of temperature units
Example 1: let's transform 45 OC for OF.
To perform the transformation, just put the data in the formula below:
TOÇ = TOF-32
5 9
45 = TOF-32
5 9
5.(TOF-32) = 45.9
5TOF - 160 = 405
5TOF = 405 + 160
TOF = 565
5
TOF = 113 OF
Example 2: let's transform 200K to OÇ.
To perform the transformation, just put the data in the following formula:
TK = TOC + 273
200 = TOC + 273
TOC = 200 - 273
TOC = - 73 OÇ
To learn more about converting values between thermometric scales, read the following text: Conversion between thermometric scales.
units of length
The most used units for working with length they are:
Kilometer (km);
Subway (m) [standard unit of length according to SI];
Centimeter (cm);
Decimeter (dm);
Millimeter (mm).
To convert one unit into another, just follow these relationships:
1 km = 1000 m
1 m = 100 cm
1 dm = 10 cm
1 cm = 10 mm
→ Conversion of units of length
Example 1: Let's transform 5 km into dm.
Analyzing the diagram, the difference between km and dm is in the order of 100000, so just set up the following rule of three:
1 km 100,000 dm
5 km x
x.1 = 5.1 million
x = 500000 dm
Example 2: Let's transform 500 mm into cm.
As 1 cm is equivalent to 10 mm, just use the following rule of three:
1 cm 10 mm
x 500 mm
x.10 = 500.1
x = 500
10
x = 50 cm
Energy units in the form of heat
The most used units for working with energy in the form of heat they are:
Joule (J) or kilojoule (KJ = 1000 J) [joule is the standard unit established by the SI];
Calories (lime) or kilocalories (Kcal = 1000 cal).
To convert one unit into another, just follow this list:
1 cal = 4.18 J
1Kcal = 4.18KJ
See some examples:
Example 1: Let's transform 2600 Kcal into KJ.
As 1 Kcal equals 4.18 KJ, just use the following rule of three:
1 Kcal 4.18 KJ
2600 Kcal x
x.1 = 2600.4.18
x = 10868 KJ
time units
Time (h);
Minute (min);
Second(s) [unit]standard of time established by the SI].
To convert one unit into another, just follow these relationships:
1h = 60 min
1 min = 60 s

Relation between time units
→ Conversion of time units
Example 1: Let's transform 6 h into seconds.
As 1 hour is equivalent to 3600 seconds (the result of the 60x60 multiplication of the difference between hours and seconds), just set up the following rule of three:
1 h 3600 s
6h x
x.1 = 6,3600
x = 21600 s
Example 2: let's transform 600 s into minutes.
As 1 minute is equivalent to 60 s, just use the following rule of three:
1 min 60 s
x 600 s
x.60 = 600
x = 600
x = 600
60
x = 10 min
Mol (amount of matter)
It is the unit that establishes the amount of entities (atoms, ions, electrons, neutrons, molecules) that form a given matter. Second Amedeo Avogadro, 1 mole of any matter contains 6.02.1023 entities.
Example: 1 mole of H2O.
One mole of the water substance has:
6,02.1023 water molecules;
3.6,02.1023 atoms (the 3 is the result of the sum of 1 oxygen and 2 hydrogens);
2.6,02.1023 hydrogen atoms;
1.6,02.1023 oxygen atoms.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/unidades-medida.htm
