Specific heat is a quantity studied by physics that relates the amount of heat received by a substance and its thermal variation.
Also called thermal capacity, this magnitude indicates the amount of heat needed for a gram of any substance to undergo a variation temperature corresponding to 1°C, in addition to indicating the behavior of the material when exposed to a heat source.
Specific heat is directly linked to the area of Physics called Calorimetry, which studies energy transfers from a body with a higher temperature to another body with a lower temperature.
In this study, the specific heat is present in the definition of the sensible heat and the thermal capacity of a material, as some phenomena can be better understood from the definition of heat specific.
And the greater the specific heat, the greater the amount of heat that must be supplied or removed from the substance, so that it has the thermal variation.
Water, for example, when compared to other substances, has the highest specific heat, corresponding to 1 cal/g.ºC.
Comparison table of specific heat values
Other substances and materials also have their own specific heat values, as shown in the table below:
| Substance | Specific Heat (cal/g.ºC) |
| Water | 1 cal/g.°C |
| Ethyl alcohol | 0.58 cal/g.°C |
| Aluminum | 0.22 cal/g.°C |
| Air | 0.24 cal/g.°C |
| Sand | 0.2 cal/g.°C |
| Carbon | 0.12 cal/g.°C |
| Lead | 0.03 cal/g.°C |
| Copper | 0.09 cal/g.°C |
| Iron | 0.11 cal/g.°C |
| Ice | 0.50 cal/g.°C |
| Hydrogen | 3.4 cal/g.°C |
| wood | 0.42 cal/g.°C |
| Nitrogen | 0.25 cal/g.°C |
| Oxygen | 0.22 cal/g.°C |
| Glass | 0.16 cal/g.°C |
Specific heat formula
To know the specific heat of substances, it is necessary to use the following formula:
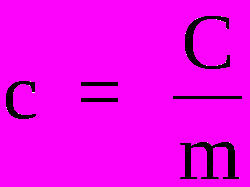
Where,
ç - specific heat (cal/g°C or J/Kg. K)
Ç - thermal capacity (cal/°C or J/K)
m - mass (g or kg)
In the International System (SI), specific heat is measured in J/Kg. K (joule per kilogram and per kelvin). However, the most used measure is in cal/g°C (calorie per gram and per degree celsius).
See also the meaning of heat and temperature.


