Table is the name of the tables that are used for facilitate basic math operations: multiplication, division, addition and subtraction.
Types of multiplication tables
As we have seen, there are tables to help with all these operations. The most used in mathematics teaching is the multiplication table.
multiplication table
The multiplication table is one of the most used in school mathematics teaching because it facilitates the resolution of multiplication accounts.
With it, you can discover the results of multiplication between numbers. See tables 1 to 10 below.

Cartesian multiplication table
Cartesian times tables are different from other times tables and is another way to solve multiplication counts. It consists of 11 columns and 11 rows.
See how to make your table:
1. In the first square, a x.
2. On the first line, write the numbers 1 through 10.
3. Do the same for the first column.
4. Repeat the same numbers in the second row and in the second column.
5. In the next lines, fill in the following tables (3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10). One trick to fill in correctly is to use the sum of the previous two squares.
Look at this example:
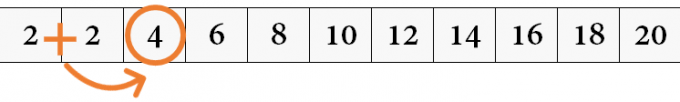
6. Now do the same procedure to fill all columns.
7. When you're done, your Cartesian multiplication table will be ready and should look like this:
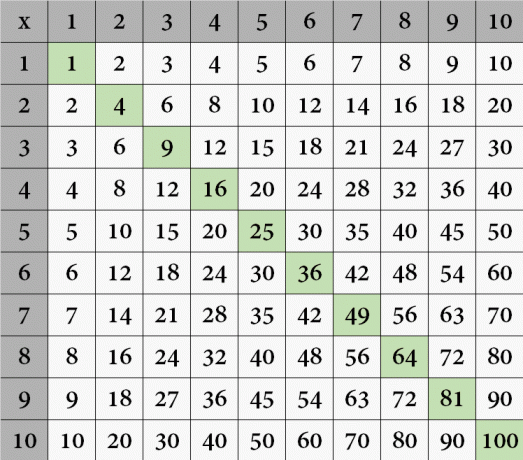 Complete Cartesian multiplication table.
Complete Cartesian multiplication table.
division tables
This is used for accounts that include divisions. See the times tables:

addition multiplication table
This times tables can be used whenever you need to solve accounts that involve sum calculations. Check out:

subtraction tables
The subtraction tables facilitate the decrement operations. Look:

Creation of multiplication tables
The idea of using multiplication tables to make accounts easier is very old. He was the Greek mathematician Pythagoras who invented the method to make it easier to find the solution of accounts and other math problems.
Pythagoras was a great student of mathematics. He created and studied other subjects in the field, such as perfect numbers. He was also the creator of the Pythagoras Theorem, which calculates the sides of a right triangle.


