the flatworms (Phylum Platyhelminthes) they are animals that live in different environments, occurring in an aquatic or terrestrial environment. Also, we have some species parasites, as is the case of tapeworms, popularly called solitary.
Platyhelminths are known as flat body worms, due to its body structure being flattened dorsoventrally. They are triblastic animals, acoelomate and with bilateral symmetry. The digestive system is incomplete and absent in some species. Excretion takes place by protonephride, gas exchange takes place by diffusion, and the nervous system is provided with ganglia.
Read too: The curious case of tapeworm cell cancer
General characteristics of flatworms
The term flatworm means flattened worm, which is a reference to the thin body of these animals, which present themselves dorsoventrally flattened. Your body is made up of three germinal leaflets (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm), therefore, are considered triblastic. They are famous animals (Do not have coelom) and present bilateral symmetry.
Flatworms are animals that have a relatively simple body, with many systems absent and others that are not very specialized. The gas exchange in these animals, for example, occurs by diffusion across the surface of the body. Concerning excretion, there is a simple system consisting of protonefrids, which are a network of tubules with ciliated structures known as flame cells.

Some flatworms have a digestive system, which is absent in other species. O digestive system of the flatworms is incomplete, the mouth being the only opening to the digestive tract. do not feature circulatory system, nor skeletal system. O nervous system it usually consists of a pair of anterior ganglia that are associated with longitudinal cords.
With regard to reproduction, it is possible to observe it in a asexual and also sexual. Many species are hermaphrodites, but there are also species of separate sexes. Some species show direct development without a larval stage, others, however, show indirect development, including one or more larval stages.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Classification of flatworms
There are different species of flatworms, some being free-living and others parasites. Among these, we can mention the tapeworms and the schistosome, while free-living, we can mention the planarian. We can identify four classes in this phylum: Turbellaria, Trematode, Basket and Monogene.
At Turbellaria we only have free-living organisms, including planarians in this group. the classes Trematode, Basket and Monogene present only parasitic representatives. in class Trematode we have as representative the schistosome; in class Basket we have the tapeworms; and on Monogene, some ectoparasitic species of fish, amphibians and reptiles.
Read too:Invertebrate animals - characteristics, groups and curiosities
Free living platyhelminths
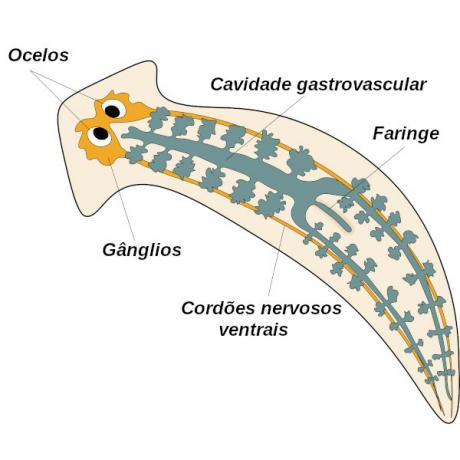
Free-living flatworms are the species that do not show parasitic habit, being found in fresh or salt water as well as terrestrial and humid environments. The best known free-living flatworm species are popularly called planarians. These animals live in freshwater environment and feed on small animals or dead animals.
The planarian has a head with a pair of ocelli — structures that guarantee light perception. On the head, side flaps are also observed, which act in the detection of chemical substances present in the Water. O nervous system of these animals it is of the ganglionic type, presenting a pair of ganglia close to the ocelli, from where ventral nerve cords depart, which run along the entire length of the body.
This animal has a digestive tube that includes a mouth, but it does not have an anus, and is therefore a incomplete digestive system. The mouth is associated with a muscular pharynx, which may protrude (move forward) from the mouth during feeding. Digestive juices are released onto the prey, and then the pharynx sucks the food into the gastrointestinal cavity, where digestion will continue. Initially, digestion is extracellular, but it is completed within cells that line the gastrovascular cavity.

THE reproduction of planarians can occur through the fission. In this case, the animal suffers constriction of its body, separating the head from the tail, giving rise to two individuals. These animals also feature amazing capacity ofregeneration. If a person cuts the planarian into several pieces, for example, they regenerate and give rise to new planarians.
THE sexual reproduction it is also observed in planarians. These animals are hermaphrodites, that is, in a single individual the production of gametes male and female. THE fertilization in this group is crossed, because, at the time of copulation, the partners are fertilized.
parasitic platyhelminths
Parasitic flatworms are well known for provoke illnesses in man, this being the case of schistosomiasis and tapeworm. In most parasitic species, there is a covering on the body that helps to protect these animals inside the host.
We'll talk more about the diseases caused by these flatworms below:
- Schistosomiasis: the schistosome (Schistosoma mansoni) is responsible for causing schistosomiasis, a disease also known as snail and water belly disease. The schistosome life cycle involves an intermediate host and a definitive host. The sick man (the ultimate host) eliminates eggs in the environment with his feces. If these feces contaminate the aquatic environment, the eggs develop into ciliated larvae called miracide, which penetrate into the interior of a host mollusc.
The miracidium undergoes some modifications and, after a few days, the mollusc starts to release a new larva, called cercaria. It is the cercaria that contaminates man if he enters a contaminated environment. After penetrating the human skin, cercaria transforms into schistosomules and, later, into an adult worm. Adult worms live in the venules of the intestine, where they will lay their eggs.
Schistosomiasis can cause weakness, lack of appetite, cough, diarrhea and swelling of the abdomen, being for this reason known as water belly.

- taeniasis and cysticerci: taeniasis is a disease caused by Taenia solium or by Taenia saginata, two species of flatworms found, respectively, in pig and ox (intermediate hosts). The man (the ultimate host) acquires taeniasis when he ingests the encysted larva (cysticercus) of these flatworms present in the contaminated meat. This larva develops into the adult form in the small intestine, where it fixes with the help of the scolex (anterior region of the body) that has fixation structures.
The man releases the calls in the feces proglottids, segments in the body of the tapeworm that contain the animal's male and female reproductive system and are capable of self-fertilization. When leaving in the feces, the proglottids contaminate the environment where they are eliminated. Intermediate hosts (pig or ox) may ingest the eggs and form cysticerci in their muscles. If a man eats the contaminated meat of these animals, undercooked or undercooked, he can develop taeniasis.
THE cysticercosis it is also caused by the tapeworm, however, this is triggered by the ingestion of eggs from Taenia solium. The eggs release the embryo, which falls into the bloodstream and can affect different parts of the body, forming the cysticercus. When it reaches the brain, we have the call neurocysticercosis.
Taeniasis can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, while cysticercosis may be asymptomatic or cause headache and convulsions, depending on where the larva is encysted.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher