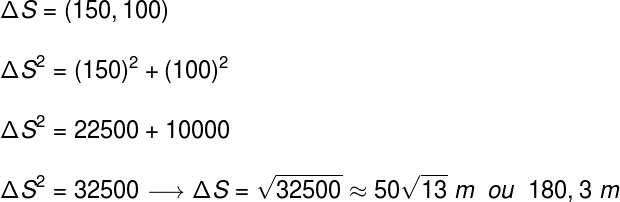cryoscopy is a colligative property that studies the lowering of the freezing point (melting point) of a solvent by the addition of a non-volatile solute such as sodium chloride or sucrose.
OBS.: Colligative properties they configure a part of Chemistry that studies the behavior of the solvent, in relation to solidification, boiling and osmosis, when a non-volatile solute is added to it.
The melting point of water, for example, is 0 OC, that is, water freezes at temperatures below 0 OÇ. However, if we add 180 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl) to 500 mL of water, it will only freeze at temperatures below -22.89 OÇ.

Presence of liquid water in a region with temperatures below 0 OÇ
In the image above, we see liquid water in Antarctica, a region of the planet whose temperatures can reach -30 OÇ. Through the study of cryoscopy, it was possible to understand why water is liquid in this region. The justification is the presence of salts in the water, which lowers its freezing point.
Formula for calculation in cryoscopy
The formula for performing the calculations in cryoscopy é:
?tc = Kc. W
- uh = is the variation of the freezing temperature or lowering of the solidification point;
- Kc = cryoscopic or cryometric constant;
- W = molality.
Each of the terms present in the general formula of cryoscopy has specific formulas, as we can see below:
a) ?tc (lower freezing temperature)
Since ?tc is a variation (?), it can be expressed as the subtraction between the freezing point of the pure solvent (θ2) and the freezing point of the solvent in the solution (θ):
?tc = θ2- θ
b) Kc (cryoscopic constant)
The cryoscopic constant is specific for each type of solvent, that is, each solvent has its constant. It can be calculated using the following formula:
Kc = RT2
1000.Lf
- R = general gas constant (0.082 in atm and 62.3 in mmHg);
- T = solvent solidification temperature;
- Lf = latent heat of fusion.
c) W (molality)
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Molality is a method of concentration of solutions and has the following formula:
W = m1
M1.m2
m1 = mass of solute (in grams);
M1 = molar mass of solute (in g/mol);
m2 = mass of solvent (in kg).
So, from the formulas above, we can rewrite the formula for the calculations in cryoscopy as follows:
θ2- θ = Kc. m1
M1.m2
Ionic solute and the cryoscopic effect
Ionic solute is any substance that, in water, can undergo the processes of ionization (production of ions) or dissociation (release of ions), increasing the amount of particles in the solvent.
Therefore, whenever we perform calculations in the cryoscopy, due to the presence of a non-volatile solute of ionic nature, it is mandatory to use the Van't Hoff correction factor (i), as in the following expression:
?tc = Kc. W.i
Example of calculation in cryoscopy
(UFMA) Find the molecular formula for sulfur knowing that adding 0.24 g of it to 100 g of carbon tetrachloride lowers the freezing temperature of CCl4 by 0.28°C. Data: Kc (CCl4) 29.8 K.kg.mol-1 .
Data provided by the statement:
m1 = 0.24 g;
m2 = 100 g or 0.1 kg (after dividing the supplied mass by 1000);
?tc = 0.28 OÇ;
Substance formula = ?
M1 = ?
1O Step: determine the molecular mass value from the data provided.
?tc = Kc. m1
M1.m2
0,28 = 29,8.0,24
M1.0,1
0.28.0.1M1 = 29,8.0,24
0.028.M1 = 7,152
M1 = 7,152
0,028
M1 = 255.4 g/mol
2O Step: determine the molecular formula (formed only by sulfur atoms - Sno) by dividing the mass found by 32 g/mol, which is the mass of sulfur.
n = 255,4
0,028
n = 7.981
or, rounding off, n = 8
Therefore, the molecular formula of the compound is S8.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "What is cryoscopy?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-crioscopia.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Colligative properties, tonoscopy, ebullioscopy, cryoscopy, osmoscopy, colligative effects, reduction of chemical potential of solvent, boiling temperature, melting point drop, osmotic pressure, non-volatile solute, solute, solvent, tempe