O principle of Le Chatelier tells us that when a disturbance is caused to a system in equilibrium, it will shift in the direction that minimizes the forces created by that disturbance and restores a new chemical equilibrium.
One of these disturbances is the temperature variation. This variation is important because, in addition to causing the equilibrium shift, it will also change the value of the equilibrium constant, Kç.
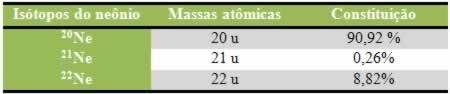
For you to better understand how this happens, let's look at an example:
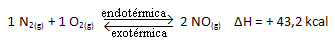
Kç = _[ AT THE]2___
[N2]. [O2]
The above reaction occurs in the direct direction with energy absorption, it is endothermic. The reverse process, on the other hand, occurs with the release of energy, being an exothermic reaction.
Thus, if we increase the temperature of the system, the chemical equilibrium will shift towards the endothermic reaction, which in this reaction is to the right. This is so that the heat is absorbed and equilibrium is regained.
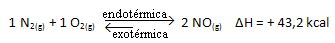
The opposite is also true; if we lower the temperature of this system, the reaction will shift in the direction that it will release heat, because the total energy of the reaction will decrease. This means that the balance will shift towards the exothermic reaction, which in this case is to the left:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
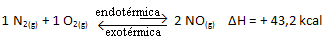
In short:

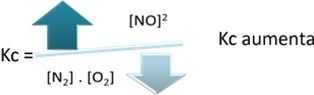
In relation to the equilibrium constant (Kç), when the temperature increases, it favors the endothermic reaction and more NO(g) is formed, increasing its concentration and decreasing the concentration of reactants. Note in the formula below that the NO concentration(g) is directly proportional to the constant Kç, therefore, it also increases:
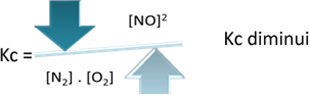
But if we decrease the temperature, shifting the reaction towards the exothermic reaction, the concentration of the NO product will decrease and the concentrations of the reactants will increase. Since the concentrations of reactants are inversely proportional to the constant Kc, then it will decrease:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Temperature Variation and Chemical Equilibrium Shift"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/variacao-temperatura-deslocamento-equilibrio-quimico.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Test your knowledge and learn more with this list of solved exercises on chemical balances. Through this material, you will be able to better understand how to work equilibrium constants (Kp, Kc and Ki), equilibrium shift, pH and pOH, as well as equilibrium in so-called buffer solutions.