THE ionization constant gives Water(Kw), O hydrogen potential(pH) it's the hydroxylionic potential (pOH) they are measures important for calculations involving chemical balance in acidic and basic solutions, as well as in determining the concentration of H ions+ and oh- of the solutions in question.
What is Kw?
The ionic product of water, or Kw (this wmeans water — water, in English), is the constant used to represent the balance generated by the self-ionization of water. Even at a very small rate, water ionizes producing H ions+ and oh-, according to the following chemical equation:
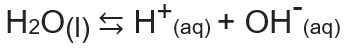
Analyzing the equation, we realize that when the ionization from a molecule of pure water an H ion is generated.+ and an OH ion-, that is, the concentration of these ions will always be the same. Even when there is an increase in temperature, which causes an increase in the ionization rate, the concentrations remain the same.
Read too:Ionization energy
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Based on experimental measurements, the concentration of H ions was calculated+ and oh- (resulting from the self-ionization of water) at 25°C and the value of 1. 10-7 mol/L. That is, of a total of 1 billion water molecules, only two undergo ionization. This shows that pure water has a low degree of ionization and explains the very low Electric conductivity of pure water.
Considering what was shown above, we can write the expression of the water balance constant:

Using H ion concentration values+ and oh- at 25°C, we can calculate the value of Kw:
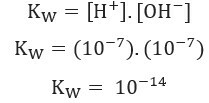
As stated earlier, this value of Kw changes with increasing temperature, as shown in the table below:
T (°C) |
Kw |
10 |
0,29. 10-14 |
20 |
0,68. 10-14 |
25 |
1,00. 10-14 |
30 |
1,47. 10-14 |
40 |
2,92. 10-14 |
60 |
9,40. 10-14 |
To learn more about this subject, read our text: Ionic water product.
What is pH and pOH?

the acronym pH means hydrogen potential and was created by the Danish biochemist Soren Sorensen, in 1909, to facilitate the work with the hydrogen ion concentrations [H+], which are usually expressed in decimal numbers. To learn more about this topic, read our text: What is pH?
This kind of notation indicates the H ion content+ present in the solution and is defined by the mathematical expression:
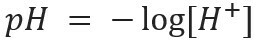
Similarly, we can define the pOH or hydroxylionic potential, which tells us the OH ion content- present in the solution. Its mathematical expression is:
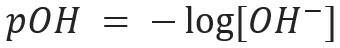
In an aqueous solution there will always be H ions+ and oh- (due to the ionization suffered by the water) that will be used to characterize a solution in acidic or basic. The more H ions+ there is in the solution, the more acidic it will be. Consequently, the presence of OH ions- in the solution will make it more basic. If there is an equilibrium in the amount of these ions, the solution will be classified as neutral.
pH scale
The pH scale is displayed with values ranging from 0 to 14 (values measured at 25°C). See the pH scale in the image below:

The lower the pHof the solution,greater is its acidity, and the closer to the end of the scale, that is, closer to 14, the greater will be its basic character. For example, lemon juice has a pH of 2, whereas bleaches have a pH of 12.
How to calculate pH and pOH
knowing the ion concentration, we can calculate the values of pH and pOH of the solutions, and, knowing the potential values, we calculate the concentration of ions in solutions. For this purpose, the following expressions are used:
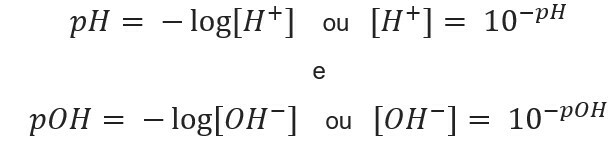
Let's go to the examples:
Example 1
If we want to know the pH of a solution with [H+] = 0.001 mol/L, just use the formula previously presented:
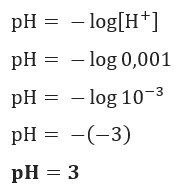
Example 2
Now, to find out what is the concentration of OH- of a solution with pOH = 5, just replace the value in the following formula:

If we apply the same scale of potentials for the ionic balance of water, we will have:
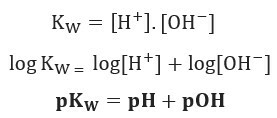
As stated, at 25°C, Kw = 10-14. Therefore:

With this, we can calculate the pOH of a solution based on its pH. If we have a solution with a pH of 3, then its pOH will be 11.
Know more: Neutral, acidic and basic media
solved exercises
Question 1 (UEFS-BA) The concentration of OH ions–(here) in a given ammonium hydroxide solution, at 25 °C, is equal to 1.10–3 mol/L. The pOH of this solution is:
a) 0
b) 1
c) 3
d) 11
e) 13
Resolution: Letter C. If we have [OH–] = 10–3 mol/L, so your pOH will be equal to 3.
Look:
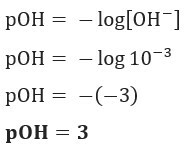
Question 2 (UEA-AM) Consider the following information, obtained from a mineral water label in the city of Porto Seguro (BA):
nitrate 1.45 mg/L
pH at 25°C 4.51
This mineral water is
a) acidic and has [H+] < [OH–].
b) acidic and has [H+] > [OH–].
c) neutral and has [H+] = [OH–].
d) basic and has [H+] > [OH–].
e) basic and has [H+] < [OH–].
Resolution: Letter B. As the pH of mineral water informed on the label is less than 7, we can say that it is an acidic solution and, therefore, the concentration of H ions+ is bigger than OH's-.
Question 3 (UEA-AM) One way to rapidly produce gaseous hydrogen in the laboratory is by reacting powdered metallic zinc with hydrochloric acid (HCl), at a concentration of 1.0 mol/L:
Zn (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Considering that the hydrochloric acid is 100% ionized and that the solution is at 25°C, it is correct to state that the pH of the hydrochloric acid solution mentioned in the text is
- 0
- 1
- 3
- 13
- 14
Resolution:Letter a. We can calculate the pH of the solution using the concentration of HCl informed in the text, since, as it is 100% ionized, the concentration of [H+] will be the same, because for each ionized HCl molecule, one H ion+ will be generated. Therefore:
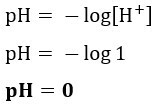
By Victor Ferreira
Chemistry teacher