The caatinga is a brazilian biome of semiarid climate located in the North East. This biome only exists in Brazil and occupies about 840 km2, which represents 11% of the Brazilian territory and 70% of the northeastern territory.
The name caatinga is of Tupi-Guarani origin and means "white forest", due to the whitish appearance of the tree trunks due to the dry climate.

This biome is present in the following states: Piauí, Maranhão, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte, Pernambuco, Paraíba, Alagoas, Sergipe, Bahia and in a part of Minas Gerais. See the area covered by the caatinga on the map:
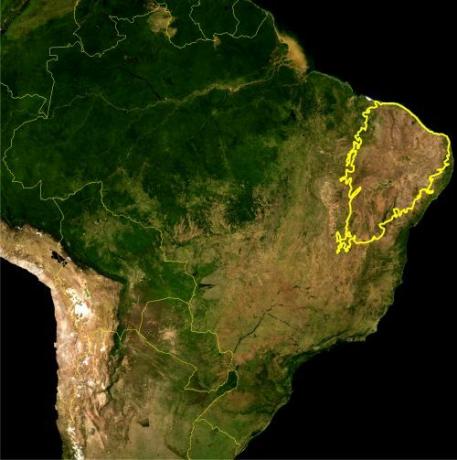
Despite the aridity of the soil and the dry climate, the caatinga is home to a great biodiversity, including species exclusive to this biome. 33% of the vegetation and 15% of the animals in this region are exclusive to the caatinga, that is, they are endemic species.
About 27 million people live in the caatinga region. The local population uses technologies such as the cistern to store rainwater, which will be used during the dry season.
Among the main economic activities in the region are the extraction of wood, cattle raising and the cultivation of sugar cane.
Characteristics of the caatinga biome
The caatinga has peculiar characteristics, its flora and fauna needed to develop ways to adapt to the scarcity of water and low air humidity.
Know what is a biome and meet the Brazilian biomes.
Caatinga vegetation
The vegetation of the caatinga is formed by xerophytic plants, that is, they are adapted to desert and semiarid climates. To facilitate water storage, plant roots often cover the ground.
The caatinga is composed of short trees and bushes and during the dry season, plant leaves fall to avoid water loss through transpiration and also to prevent photosynthesis, thus providing energy savings.
When the rains start, the leaves reappear, turn green and bloom.
There are species of cacti in the region, such as the mandacaru, which has thorns that, in addition to working as defense mechanisms, are leaves modified to prevent the process of transpiration.
Among the species of the caatinga flora are the juazeiro, the purple ipe and the macambira.
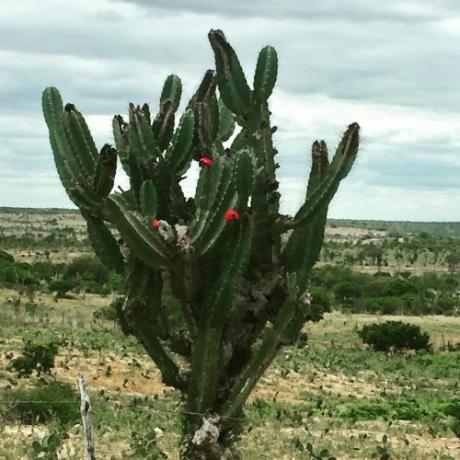 Mandacaru (Cereus jamacaru)
Mandacaru (Cereus jamacaru)
Caatinga climate
The climate of the caatinga is semi-arid, with alternating periods of rain and dry periods. The drought periods are longer, the number of months without rain in the region can reach eight or nine.
Due to the low rainfall in the caatinga, the relative humidity of the air is low and temperatures usually vary between 25º C and 30º C throughout the year.
See the meaning of climate.
caatinga fauna
The caatinga has a wide variety of mammal, amphibian, bird, reptile, fish and insect species. Brazilian fauna, including the lizard calanguinho, the rattlesnake, the carcará bird, the jaguar and the capuchin monkey.
See the number of species of fauna in the caatinga.
| Mammals | birds | reptiles | amphibians | Fish | bees |
| 178 | 597 | 177 | 79 | 241 | 221 |
 Rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus)
Rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus)
Due to the deforestation of this biome, some animals are or are at risk of extinction. The blue macaw, for example, has already been declared extinct by IBAMA, and the brown deer is a species that is at risk of extinction.
 Brown deer (Mazama gouazoubira)
Brown deer (Mazama gouazoubira) Capuchin Monkey (Sapajus)
Capuchin Monkey (Sapajus)
See the meaning of fauna.
Caatinga soil
The soil of the caatinga is clayey and sandy, it is poor in organic matter, but rich in minerals, which gives it reasonable fertility. It is due to these ores that dry vegetation quickly turns into grasses and green leafy plants when it rains.
Caatinga hydrography
The rivers that originate in the caatinga are intermittent and temporary, that is, they dry up in periods of drought and reappear when the rain arrives.
The only perennial rivers that supply the region are the São Francisco River and the Parnaíba River, which originate elsewhere but cross the caatinga region.
 São Francisco River in Paulo Afonso, on the border between Bahia and Alagoas.
São Francisco River in Paulo Afonso, on the border between Bahia and Alagoas.
Deforestation of the caatinga
Deforestation and burning are a threat to this biome, which is already lost 46% of its original coverage. Deforestation of the caatinga is done, above all, for the use of land for agriculture and pasture.
Another threat to the caatinga is hunting and illegal trade in wild animals.
The destruction of this biome has numerous negative consequences for the balance of ecosystems, the maintenance of species and for the quality of water in the region.
See also the meaning of logging, endangered species and preservation of the environment.


