Fallfree is a vertical movement that consists of falling bodies without the effect of frictional force. Here on Earth some bodies that fall from small heights in relation to the ground do so in a way close to an ideal free fall.
What is free fall?
The free fall movement was studied by the Italian physicist Galileo Galilei. According to his studies, Galileo showed that bodies in free fall, even those of different masses, would reach the ground at the same time, as they would be subject to the same acceleration. Free fall is, therefore, a movement described by bodies, abandoned at a certain height, which happens exclusively due to the effect of gravity local. In this type of movement, we disregard the effect of forcesindragorfriction.
See too: 8 fundamental Physics formulas for the Enem test
The free fall is a uniformly varied movement, that is, a body in free fall has its velocity increased at constant rates. When a body is abandoned at heights near the Earth's surface, the speed at which it falls increases at a rate of 10 m/s, which is the same as saying that the acceleration of the Earth's gravity is 10 m/s², about 36 km/h each second.
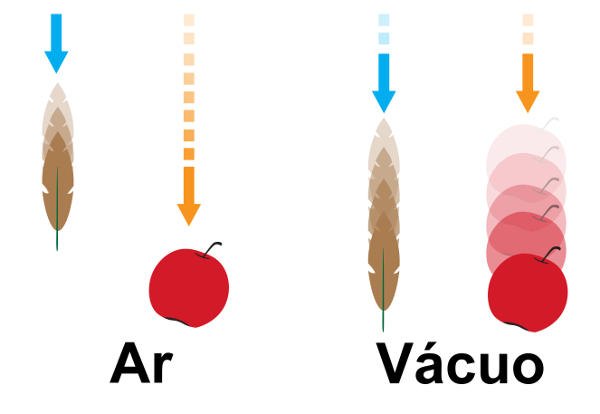
free fall examples
Any heavy bodies that have a small area of contact with air can describe a very close movement to what is meant by fallfree, if loose at small heights in relation to the ground. Check out some examples:
A bowling ball dropped at hip height;
A heavy book that falls from the surface of a table;
A wheel wrench that falls out of the trunk of a car;
A cell phone that falls out of a jacket pocket.
Despite being movements very close to the situation of a free fall, it only actually happens in bodies that are abandoned in the vacuum in regions where there is accelerationgravitational.
free fall form
At fallfree, assuming that the body is abandoned at a certain point, that is, it is initially at rest, the equations to be used will be these:
Equation of body velocity in free fall:

v – fall velocity (m/s)
g – gravity acceleration (m/s²)
t – time interval(s)
The equation above is used to determine the velocity where a body moves during the free fall movement. To do so, just multiply the time of fall, measured in seconds, with the magnitude of the acceleration of gravity.
Height equation in free fall:
The following equation relates the fall height to the time interval:

H – height (m)
Through the equation shown above, it is possible to determine both the height how much the timeinfall of a body in free fall.
Torricelli Equation
In addition to the two formulas shown, we can use an equation that relates to velocity of fall with the height, a Torricelli equation.
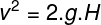
Lookalso: Everything you need to know about Newton's Laws
Free Fall Graphics
How the free fall movement is of the type evenlymiscellaneous, your graphics of velocity and position they are, respectively, an ascending straight line and a parabola, with the concavity facing upwards. Look:

Free Fall Fixed Exercises
Question 1) Knowing that a body takes 2 s to reach the ground after being dropped at a height H in relation to the ground, calculate the height at which that body was dropped, in meters.
a) 20 m
b) 15 m
c) 30 m
d) 40 m
e) 80 m
Template: Letter a
Resolution:
The exercise asks us to calculate the drop height and tells us the time. In this way, just use the formula that relates these two quantities.

Question 2) A basketball is dropped at a height of 5 meters from the ground. If this ball is moving in free fall, what is the speed of the ball, in km/h, just before it touches the ground?
a) 50 km/h
b) 10 km/h
c) 36 km/h
d) 15 km/h
e) 10 km/h
Template: Letter C
Resolution:
The exercise asks us to find the speed of the ball, however, its statement does not tell us the time of fall, so we will use the Torricelli equation, as shown in the following calculation:
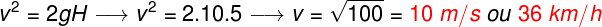
After finding a speed of 10 m/s, it was necessary to multiply the result by a factor of 3.6 to transform it to the unit of kilometers per hour.
Question 3) An object is dropped at a certain height from the ground, describing a free-fall movement. Assuming that the acceleration of local gravity is 10 m/s², what is the time, in seconds, for this object to reach a speed of 108 km/h?
a) 2 s
b) 4 s
c) 3 s
d) 5 s
e) 8 s
Template: Letter C
Resolution:
The exercise asks us to calculate the time it takes for a body in free fall to reach a speed of 107 km/h. To make this calculation, we will transform the unit from km/h to m/s, dividing this speed by 3.6; then we'll use the free fall speed formula:
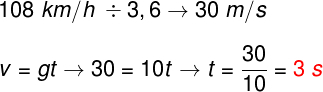
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock
