What does it mean to say that a gas has undergone a gaseous transformation?
To answer the initial question, it is important to remember that the state of the gas or gaseous state is determined by the state variables: pressure, volume and temperature. Soon, a gas transformation it is nothing more than any situation in which a certain amount of gas undergoes variation in one of its three state variables. Whenever a variable undergoes change, another one will consequently have its value changed.
In the 17th century, several scientists carried out experiments in order to discover the particularities of gas transformations. Among them, we can mention: Torriceli, Robert Boyle, Mariotte, Guericke, among others. In his studies, the procedure consisted of changing one of the state variables and observing the behavior of the others. In doing so, they observed that to significantly determine the relationship between a variable and another, it was necessary to make the third one not change, that is, to remain constant. Thus, the investigations were carried out in three different ways, each with its particularities, they are:
isothermal transformation, isobaric transformation and isovolumetric transformation.Before detailing the three transformations mentioned above, let's remember what the General Perfect Gas Law: According to this law, a mass of gas initially defined by state variables (p1,V1 and T1), when undergoing a gaseous transformation, it has the state variables (p2,V2 and T2) that characterize the final state of the gas. These variables follow the following relationship:

From the above equation we can see that pressure, volume and temperature vary during the gas transformation.
Isothermal transformation orBoyle-Mariotte's Law: is the transformation in which the temperature T of the gas remains constant, varying its pressure P and its volume V. The following list is valid:

Isobaric Transformation orGay-Lussac Law: is the transformation in which the pressure P of the gas remains constant, varying its volume V and temperature T. The following list is valid:
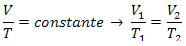
Isovolumetric Transformation or Charles Law: also known as isometric transformation, is the transformation in which the volume V of the gas remains constant, varying its pressure P and temperature T. The following list is valid:

By Nathan Augusto
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/as-transformacoes-gasosas.htm

