Natural selection is one of the main points of theory proposed by Charles Darwin. According to natural selection, the fittest organism survives and passes on its characteristics to offspring, thus ensuring that advantageous characteristics are fixed in a population. We can divide natural selection into three types: stabilizing, directional, and disruptive.
Read more: Charles Darwin – life, marriage, education, work and death
What is natural selection?
Natural selection is the evolutionary mechanism proposed by Charles Darwin, who stated that the environment acts as a feature picker, perpetuating the organisms best able to survive in a given location.
The most adapted organisms can survive and produce offspring, which inherit these characteristics. Less adapted organisms have a lower chance of survival and, consequently, of reproduction. Thus, over time, it is clear that the most advantageous characteristic increases in the population.

It is noteworthy that there is no trend towards improvement according to the individual's needs. THE natural selection acts only on existing characteristics in a population, not causing the emergence of better characteristics.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Example of natural selection
To understand natural selection, let's imagine, for example, the following situation: in a snowy place they are observed white fur rodents and brown fur rodents. Whites are able to hide in snow easily through the camouflage. Browns, on the other hand, are not able to hide so easily, being easily spotted by predators.
As whites are less captured, they have a greater chance of surviving as well as reproducing. With that, the characteristic of the white coat is being passed on to the next generations and increasing in the population, while the brown coat is decreasing, as these animals have a lower chance of survival and reproduction.
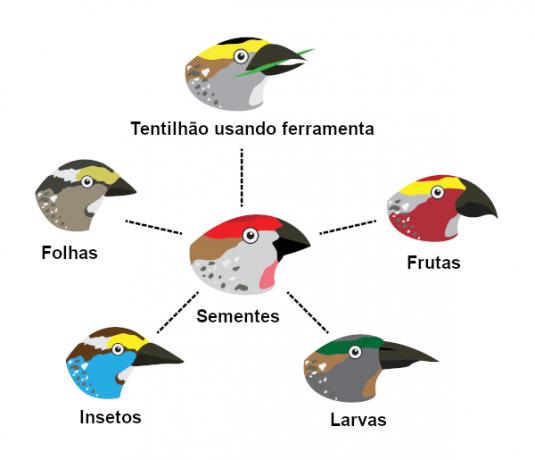
Natural selection can also be verified when we analyze the finch beaks, birds Darwin observed in the Galapagos Islands during his famous voyage aboard the Beagle. Darwin noted that there were different finches on each of these islands, being distinguished, among other features, by their beaks.
The scientist concluded that the finches that occupy the islands are probably derived from the same original species, however they are subjected to different pressures on each island. As the islands have ecological environments distinct from each other, the environment ends up selecting the most adapted organisms to those environments, which provide different diets.
Read too:Genetic variability - fundamental for the occurrence of natural selection
Types of natural selection
Natural selection can be divided into three types: stabilizer, directional and disruptive. It is worth noting, however, that, regardless of the type of selection we are referring to, everyone acts to ensure that the fittest survives.
- Stabilizer selection: acts against two extreme characteristics, favoring intermediate characteristics. A classic example is the weight of human babies. Natural selection acted by selecting babies from 3 kg to 4 kg. Very small or very large babies are at greater risk of mortality, so their frequency in the population has decreased over time.
- Directional selection: occurs when one of the extremes is favored. Directional selection acts, for example, in the case of the aforementioned white and brown rodents. The characteristic of the white coat was selected, while the different shades of brown were reduced as they were not advantageous in that environment.
- Disruptive selection: two extremes are favored. Intermediate characteristics in this case are not selected. An example is that of the African finches from the Republic of Cameroon. In this region, individuals with very different beak sizes are observed. Animals with small beaks feed on soft seeds, while those with large beaks feed on harder seeds that can be broken with their beaks. The intermediate size nozzle, as it is not as efficient as the others, is not selected.
If you want to go deeper into the topic of this topic, read: Types of natural selection.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Natural selection"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/selecao-natural.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.