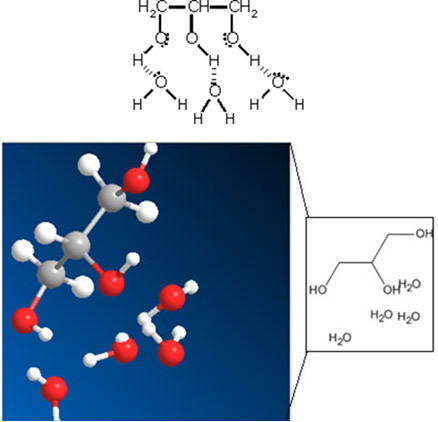
Nicotine is an organic compound from the group of alkaloids, that are heterocyclic amines, that is, they have closed chains (cycles), containing a nitrogen. Its structural formula is shown below:
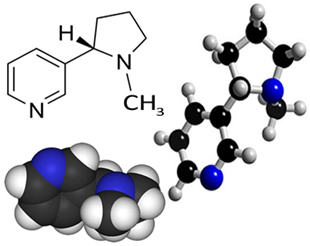
As an amine, nicotine has a basic character and appears (at room temperature and in its pure form) as an oleaginous and colorless liquid. However, in contact with air, this liquid oxidizes, turning dark brown. It is soluble in water and very soluble in organic solvents such as ether and alcohol.
So, like other alkaloids, nicotine has a bitter taste and is very toxic. It is found in tobacco plants, from which tobacco is produced, in a concentration ranging from 2% to 8%.

It is produced in the burning of cigarettes and is the main cause of dependence that the smoker presents. This is because, when you inhale a cigarette, nicotine reaches the brain in about 9 seconds and acts on the central nervous system, causing a pleasant feeling of well-being. However, this feeling is temporary and the more a person smokes, the more the body adapts to the drug and addiction increases, requiring more doses of nicotine in the body, that is, increasing the amount of cigarettes consumed. That's why when someone tries to stop the addiction, suddenly stopping smoking cigarettes, she usually has a
withdrawal syndrome.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
In addition, at the time of consumption, nicotine also causes a stimulating action in the central nervous system and, as a consequence, there is the increased blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate and motor activity, in addition to reduced appetite.
When the cigarette is inhaled, the nicotine is immediately distributed to the tissues and is absorbed by the lung. As a result, countless damages are caused to the body, see some:

THE lethal dose average nicotine for a human is between 40mg to 60mg, being that only a cigarette already contains about 0.6 mg.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Nicotine"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/nicotina.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Meet the alkaloids, a class of amine compounds that are very important, as they are present in everyday life, such as nicotine, caffeine, morphine and cocaine.
Amines, classification of amines, amine properties, primary amine, nitrogenous organic compounds, alkyl radicals, dimethylamine, ethylamine, trimethylamine, compounds extracted from vegetables, putrescine, cadaverine, organic bases, syntheses organic
Chemistry

Caffeine, Amphetamine, Cocaine, Crack, amines, increased nervous system activity, reduced appetite, caffeine, intense depression, hydrochloride, motor activity, guarana powder.
Chemistry

How does electronic cigarette work, toxic substances, pure nicotine, cadmium, arsenic, vaporization chamber, reducing smoking, cigarette without tobacco, alternative for those who want to quit smoking.