In vascular plants we observe the presence of two types of conduction tissues: the xylem and the phloem. O xylem is related to the conduction of water and inorganic nutrients from the plant, in addition to storing some substances and acting with the sclerenchyma it's the collenchyma in supporting the body of the vegetable. already the phloem it is a tissue related to the transport of organic substances.
Xylem
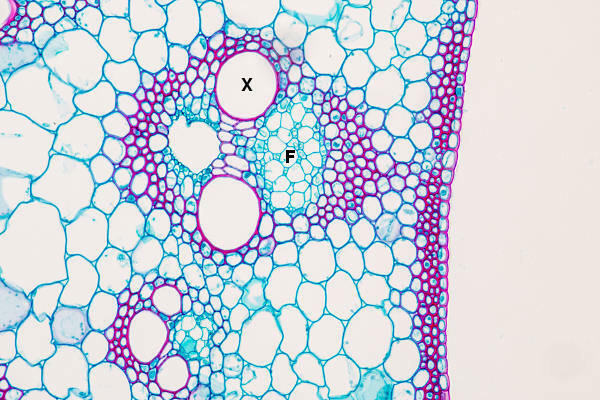
O xylem, also called wood, is a conduction tissue that has the tracheids and vessel elements as the main conduction cells. These cells, known as tracheal elements, are characterized by being dead in maturity and because they have lignified secondary walls.
At tracheids are found in all groups of vascular plants, especially in the pteridophytes and gymnosperms. These cells have pits (an area without a secondary wall) on their walls and are considered to be less specialized than the vessel element.
O vessel element is found mainly in
angiosperms, although it occurs in some groups of gymnosperms. It is considered more specialized than tracheids because it has perforations (areas without primary and secondary walls) in its walls, which favors the fluidity of water. These elements are joined at their ends, forming continuous tubes.In addition to the vessel and tracheid elements, the xylem has parenchymal cells and some fibers, being, therefore, considered a complex tissue. Parenchymal cells are associated with storage of substances, while fibers are associated with support and storage.
Primary and secondary xylem
O primary xylem occurs in plants in primary growth (growth in height), while the secondary xylem appears in plants in secondary growth (growth in thickness). Both the primary and the secondary xylem have the same cell types, however, in the first, cell types are organized in the axial system (vertical), while in the second the cell types are organized in the axial and radial systems (horizontal).
Another important difference between primary and secondary xylem concerns its origin. While that one originates from the procambio, this is formed on the call vascular exchange.

Read more:Growth rings: relationship between the action of xylem and the appearance of these rings in plants
Phloem
Unlike xylem, phloem tissue cells present living protoplast in maturity. The phloem, also called liber, has two types of conducting cells, known as crimped elements: the sieve cells and the elements of the sieve tube. The name of these types is linked to the presence of small pores known as sieves. The sets of sieves are called screened areas.
In the screened cells Small pores are found, and the crimped areas are located mainly at the ends of these cells. The sieved cells are considered less specialized than sieved tube elements and occur in pteridophytes and gymnosperms.
US sieve tube elements, the pores are relatively larger than in sieved cells. The areas screened with larger pores are called crimped plate, which usually occurs at the ends of the sieve tube elements. These conductive cells are found only in angiosperms.
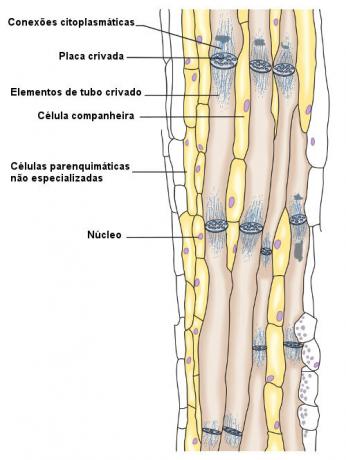
The elements of the sieve tube are always closely associated with parenchymal cells, which are called companion cells. It is believed that these act by coordinating activities of the elements of the screened tube. When one of them dies, the other also stops working.
In gymnosperms, parenchymal cells associated with crimped cells also occur. The first, called albuminous cells, apparently perform the same functions as the companion cells.
Like the xylem, the phloem has different cell types and is, therefore, a complex tissue. Parenchymal cells, fibers and sclereids are found in this tissue.
Primary Phloem and Secondary Phloem
The primary phloem is found in primary growing plants and is originated from the activity of the prochange. The secondary phloem, found in plants in secondary growth, originates from the action of vascular exchangea. Like the secondary xylem, the secondary phloem differs from the primary in that it is organized in radial and axial systems.
Also access:Cytology - the area of biology that studies the structure of cells
Arrangement of xylem and phloem in the plant
The conducting tissues occur in practically all the organs of the plant, forming a kind of continuous system that runs through the entire plant. At the root, the phloem alternates with the xylem. In the stem, normally, the phloem is in the most external position in relation to the xylem. In leaves, the phloem is found facing the abaxial face.
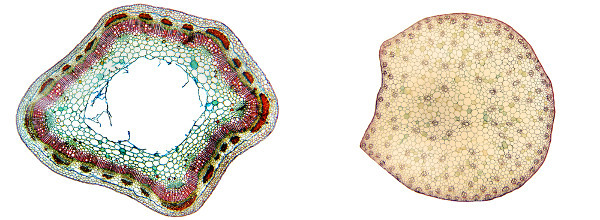
An important feature that allows differentiating the stem of a monocot from a eudicot is the disposition of the vascular bundles (xylem and phloem). In the monocots, the beams are randomly arranged in the parenchyma. In eudicots, the bundles are distributed in a ring.
Know more:Reino Plantae - know the classification of vegetables
Xylem and Phloem Exercises
Here are two questions on the subject of xylem and phloem:
question 1 |
|
(IF-Southeast-MG) Xylem and phloem are the tissues responsible for transporting substances in plants. Review the statements about these fabrics and tick the correct alternative. a) Insects that parasitize leaves suck food directly from the xylem. b) Hemiparasitic plants suck elaborated sap from the xylem. c) Xylem is the tissue responsible for transporting the sap produced from the leaf to the root. d) Phloem is the tissue responsible for transporting raw sap from the leaf to the root. e) Holoparasitic plants suck elaborate phloem sap. |
Resolution of question 1: letter e. A holoparasitic plant gets all the nutrients necessary for its survival from the host plant. As the phloem is responsible for transporting organic substances, these plants take their nutrients from this tissue.
question 2 |
|
(UFJF) The variegated chlorosis of orange trees, known as yellowing, is caused by a bacterium that, after installed, it multiplies and obstructs the tissue responsible for carrying water and nutrients from the roots to the aerial part of the plant. Among the symptoms of the disease is the reduction in the size of the fruits, making them unfeasible for consumption. Tick the alternative that presents tissue clogged by bacteria. a) Aquifer parenchyma b) Chlorophyllian parenchyma c) Collenchyme d) Xylem e) Phloem |
Resolution of question 2: letter D. As the bacteria obstruct the tissue responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the root to the shoot, the issue concerns the conduction tissue called xylem.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/xilema-floema.htm

