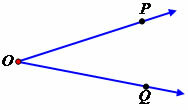
We call the opening formed by two semi-straight lines that have the same origin by angle.
The usual unit of angle is degree (represented by °), for example:
25th: read twenty-five degrees.
32º: reads thirty-two degrees.
120º: reads one hundred and twenty degrees.
90º: reads ninety degrees.
The degree has two submultiples: the minute (represented by ’) and the second (represented by ). Watch:
32’: reads thirty-two minutes.
81’: reads eighty-one minutes.
15”: reads fifteen seconds.
45”: reads forty-five seconds.
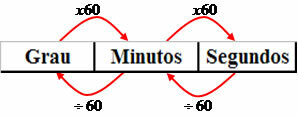
We have that 1st (one degree) corresponds to 60’ (sixty minutes) and 1’ (one minute) corresponds to 60” (sixty seconds). For example, look at the following transformations:
2nd in minutes: 2 * 60 = 120’
12’ in seconds: 12 * 60 = 720"
3600’’ in minutes: 3600: 60 = 60’
90000" in degrees: 90000: 60 = 1500’ and 1500: 60 = 25º
Observation:
Conversion table
Addition
Given the angles of 6º 25’ 36" and 4º 40’ 30", the sum between them is:
The result of the sum is 10º 65’ 66”, but we can present the result in another way. Follow the demo:
In the measurement angle 10º 65’ 66", we have that 65’ = 60’ + 5’ = 1º + 5’ and 66" = 60" + 6" = 1’ + 6". Thus, 10º 65’ 66" = 11º 6’ 6".
Subtraction
Given the angles 54º 16’ 32" and 27º 18’ 40", the subtraction between them is:

Note that there are values in the minuendum that are smaller than the values in the subtraend, when this happens in the subtraction, we have to remove the value on the left by completing what is smaller.
When removing 1’ from 16’ we will have 15’, where 1’ = 60” which must be added to 32” resulting in 92”.

Now we must take 1st out of 54th which will be equal to 53rd, considering that 1st = 60’, we have 60’ + 15’ = 75’. Therefore:

The result of the subtraction is equal to 26º 57’ 52".
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
plane geometry - Math - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Marcos Noé Pedro da. "Addition and Subtraction of Angles"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/adicao-subtracao-angulos.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.