Division is one of the four fundamental operations of mathematics. We divide in order to split or separate into several parts, by dividing one number by another we can generate remainder or not, if the remainder is zero, the division is exact, if not, then the division is not exact.
Recall the structure of the division algorithm:

The division algorithm can also be structured as follows:
D = d. what + r
D = Dividend
d = divider
q = Quotient
r = rest
Across the division, the numerical value of the rest will always be less than the number for the divider.
Rest < Divider
r < d → (It reads: The rest is smaller than the divisor)
We will solve four examples in order to better understand what the remainder is for exact and non-exact division.
Example 1
Find the rest of the division, if there is.

To check if the division is correct, do:
D = d. what + r
D = 4. 6 + 2
D = 26
Dividend = 26; Divider = 4; Rest = 2, Quotient = 6
the rest of the division from 26 through 4 is 2; this is a non-exact division
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Example 2
find it out the rest of the division 243 by 5 and say whether the division is exact or not.

When dividing 243 by 5, the remainder is 3. This is a non-exact division. To take the real test, do:
D = d. what + r
D = 5. 48 + 3
D = 243
Dividend = 243; Divider = 5; Rest = 3, Quotient = 48
Example 3
Is the division of the number 124 by the number 2 exact or not?

This division is exact because the remainder is zero.
Example 4
The history teacher needs to organize 50 students into groups so that these groups have the same number of students. How should he proceed?
To solve this example we must find the divisors of 50.
Dividers of 50 = { 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50}
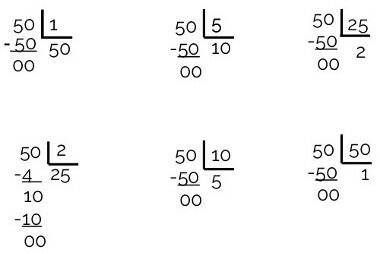
We can see that in all cases of division the remainder is zero, so the division is exact.
Final answer: The teacher can organize students into 2, 5, 10 or 25 groups.
By Naysa Oliveira
Graduated in Mathematics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
OLIVEIRA, Naysa Crystine Nogueira. "The rest of the division"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/o-resto-divisao.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.