The study of the strength of a acid is very important for determining the ability of the acidic solution to conduct electrical current, as this relates to the amount of ions that this substance produces when in contact with water (ionization). When an acid is too strong, it produces too many hydronium cations (H3O+) and many anions (X-). See the hydrobromic acid ionization equation:
HBr + H2O → H3O+ + Br-
When ionizing, the hydrogen present in the acid molecule interacts with the water molecule and forms hydronium. But for this event to happen, the hydrogen atom must necessarily be ionizable. Ionizable hydrogen is that capable of forming a hydronium cation.. To find out if a hydrogen is ionizable, we take into account the classification of the acid as hydracid (has no oxygen in its composition) or oxyacid (has oxygen in its composition).
a) Hidracids
All hydrogen in a hydracid is considered ionizable.
Examples:
- HCl: An ionizable hydrogen, thus producing a hydronium;
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
- H2S: Two ionizable hydrogens, then produce two hydrons
b) Oxyacid
In an oxyacid, only hydrogen that is bonded to an oxygen atom in the molecule is considered ionizable. For this, it is necessary to build its structural formula. See some examples:
H3DUST4 (phosphoric acid)
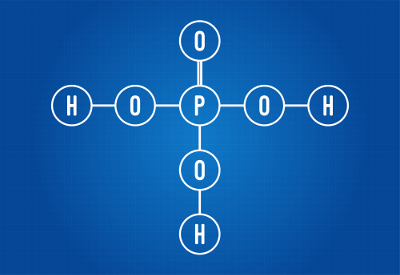
Structural formula of phosphoric acid
We can see that, in the structure of phosphoric acid, there are three hydrogens bonded to oxygen, so there are three ionizable hydrogens. The ionization equation will be:
H3DUST4 + 3 H2O → 3 H3O+ + PO4-3
H2ONLY4 (sulfuric acid)
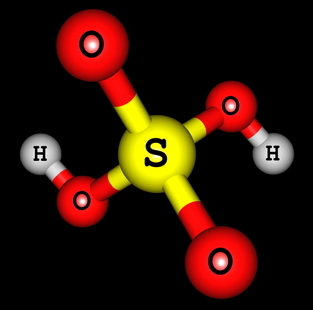
Structural formula of sulfuric acid
We can see that, in the structure of sulfuric acid, there are two hydrogens bonded to oxygen, so there are two ionizable hydrogens. The ionization equation will be:
H2ONLY4 + 2 H2O → 2 H3O+ + OS4-2
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Ionizable Hydrogens"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/hidrogenios-ionizaveis.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Dissociation and Ionization, Italian Scientist Volta, Electric Current, Swedish Physical Chemist Svant August Arrhenius, Theory of Arrhenius, positive ions, cations, negative ions, anions, caustic soda, table salt, polar molecules, dissociation ionic,


