Geometric isomerism or cis-trans it is a type of spatial isomerism, also called stereoisomerism and, therefore, the compounds that present this type of isomerism are called stereoisomers. It only occurs in aliphatic (open-chain) molecules that have a double bond or in cyclic compounds.
In unsaturated open chain compounds, if the atoms that bond to the carbons of the double are different between each other and equal to the ligands of the other carbon atom, we will have the formation of two isomeric compounds between them, a cis and another trans.
To determine if a stereoisomer is cis or trans it is necessary to know the spatial arrangement of the atoms that make up its molecules.
Let's look at the example of 1,2-dichloro-ethylene:
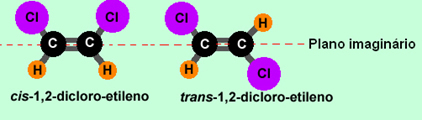
Note that in the first case the same ligands are on the same side of the plane, being isomers cis. In the second molecule, the equal ligands are on opposite sides of the plane and are therefore isomers. trans.
This difference in the spatial location of its atoms makes the compound cis have different properties than its isomer trans.
Therefore, it is concluded that in aliphatic (open-chain) compounds, for geometric cis-trans isomerism to occur, it is necessary that the compound has at least one double bond between carbons and each of the carbons in the double must have different bonding groups.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
But if all the ligands are different, how do you know which one will be cis and which will be trans?
In that case, the atomic number of ligands is considered. If the two ligands that have the highest atomic numbers are on the same side of the plane, the isomer will be cis. However, if they are on opposite sides, it will be called isomer trans.
For example, in the case of the 2-chloro-2-butene molecule, on the first carbon the ligand with the highest atomic number is Cl, and on the second carbon the ligand with the highest atomic number is CH3. So we have:
ClCH3Cl H
│ │ │ │
C C C
│ │ │ │
H3C H H3Ç CH3
Cis-2-chloro-2-butene Trans-2-chloro-2-butene
To know how this type of stereoisomerism occurs in cyclic compounds, read the text: “geometric isomer cis-trans in cyclic compounds”
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Geometric or cis-trans isomers"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/isomeria-geometrica-ou-cis-trans.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
b) Make the spatial formula of each compound that presents geometric isomerism.