THEosmosis and the solvent passage, from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution, through a semipermeable membrane, until the pressure exerted by the solution on the membrane prevents the passage of solvent. This process is intended to balance the concentration of the solution.
Read too: Solute and solvent
osmotic pressure
THE osmotic pressure and the pressure exerted on the solution with greater concentration so that osmosis does not occur, that is, so that the solvent does not cross the semi-permeable membrane.
Osmotic pressure is used in processes of water desalination, forcing the process of reverse osmosis, causing the solvent to pass from the more concentrated solution to the less concentrated one. We call this process reverse osmosis. See the following image that compares the two processes:
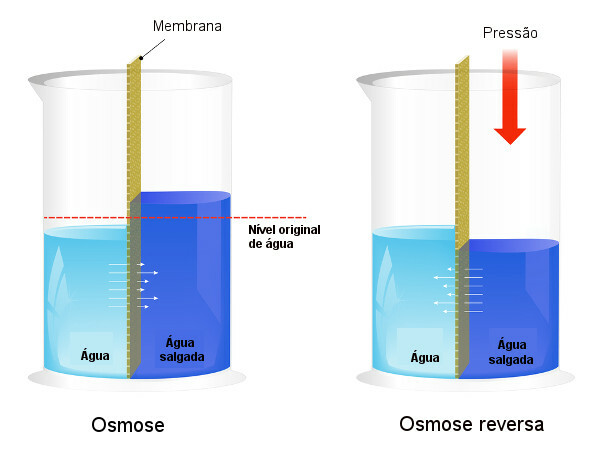
Note that, in osmosis, the passage of solvent is in the direction of the most concentrated solution and that, in reverse osmosis, the passage is in the opposite direction, due to the applied pressure. To learn more about the topic, read our text:
osmotic pressure.know more: Reverse osmosis in the desalination of seawater
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
osmotic pressure equation
Osmotic pressure, represented by the letter pi (π) of a solution, can be calculated by the following equation:
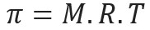
M = concentration in mol/L
R = universal constant of perfect gases
T = absolute temperature, in K
like others colligative properties, the osmotic pressure depends on the solution concentration, that is, the greater the concentration of the solution, the greater the effect of osmosis on the solutions and, therefore, the greater the osmotic pressure.
Examples
Osmosis appears in our daily lives at different times. We can cite the example of meat salting process to your conservation. You microorganisms that would cause meat degradation lose waterfrom the inside to the outside, which has a concentration of salt, making the food last longer.
Due to the salt, it also happens that the leaves of a salad wither for losing water from the inside of their cells (kind of less concentrated) for the tempered solution in the external environment.
Osmosis is also important when we talk about blood human. We say that the Red Cells and the blood is one isotonic medium, that is, they have the same osmotic pressure, allowing the entry and exit of water from the cell with ease.
However, when the blood becomes less concentrated than inside the red blood cells (hypotonic medium), the passage of water will occur more easily inside the cell, making it swell until burst. If the blood reaches a concentration greater than the concentration of the red cell (hypertonic medium), the blood cells wither, as they lose water.

By the same principle of meat conservation, the fruit conservationin the candy compotes, who preserve food due to high sugar concentration in the solution.
The following are other examples where osmosis occurs:
- in the rise of sap in the plant's conducting vessels;
- at hemodialysis;
- in the selective passage of nutrients in the cells of the human body.
To understand how osmosis happens in the animal cell, the plant cell and other biological issues, read: Osmosis: what it is and how it occurs in the animal and plant cell.
By Victor Ferreira
Chemistry teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FERREIRA, Victor Ricardo. "Osmosis"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/osmose.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.