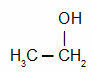O mineral coal, also called natural charcoal, it is a fossil fuel obtained through the fossilization of wood. Wood is basically made up of hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and carbon (C), but over time, hydrogen and oxygen are eliminated in the form of water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). In this way, the mineral coal, which is a mixture of complex substances rich in carbon.
Depending on the composition and mainly on the percentage of carbon, four types of mineral coals are formed:
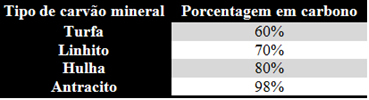

Among the types mentioned, the coal it is one of those with greater commercial importance, because through its dry distillation in the absence of air, three fractions of wide application are obtained, which are:
- Gas fraction: Contains hydrogen, methane and carbon monoxide, being used as fuel and for gas street lighting;
- Net fraction: It contains two parts, ammonia water, which is used mainly to produce fertilizers, and coal tar, which is fractionated. in five parts, being used for the most diverse applications, such as the production of paints, medicines, plastics and flooring asphalt;
- Solid fraction: Contains coking coal used in steel industries to produce iron and steel.
With the Industrial Revolution, initially coal became the most important source of energy in the world, as the heat generated in its burning was used in the production of steam that moved machines, locomotives and ships.

Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
However, coal was later surpassed by another fossil fuel, oil. This was due to some inconveniences of using coal. For example, its burning generated ash and its transport is more difficult, as it is solid, it occupies large spaces.
Furthermore, coal is highly polluting, because it has a high sulfur content, releasing sulfur oxides, such as SO2 and SO3, that go into the atmosphere and react with rainwater, making it dangerously acidic.
s(s) + O2(g) → OS2(g)
ONLY2(g) + H2O(1)→ HSO3(aq) (sulfur acid)
ONLY2(g)+ ½ the2(g) → OS3(g)
ONLY3(g) + H2O(1)→ H2ONLY4(aq) (Sulfuric acid)
Despite this, coal is still used to generate electricity, mainly in North America and Europe. However, care must be taken not to release sulfur oxides into the atmosphere.
Unfortunately, fossil fuels, whether coal, oil and its derivatives, or natural gas, when burned, release polluting gases into the atmosphere. In the complete combustion of fossil fuels, carbon dioxide is released, which has contributed strongly to environmental problems such as global warming.
Another problem with coal is that it not a renewable energy source, with estimates being that our reserves will last just over two centuries.
An energy alternative to coal is the charcoal, which is obtained through the incomplete combustion of wood by controlling the intake of air. It is a good fuel because, in addition to being cheap and plentiful, it is also renewable.

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Chemistry

Oxides and the Environment, carbon dioxide, petroleum-derived fuels, natural gas, photosynthesis that plants carry out, forest vegetation, seaweed, fires, Greenhouse effect, global warming, infrared radiation, chlorofluor