Logarithm is a mathematical function that is based on the potentiation and exponentiation properties. The logarithm value corresponds to the exponent to raise a certain base, positive and different from 1, so that the result is equal to a positive number b.
To better understand the concept of the logarithm, it is necessary to observe the logarithmic equation formula:
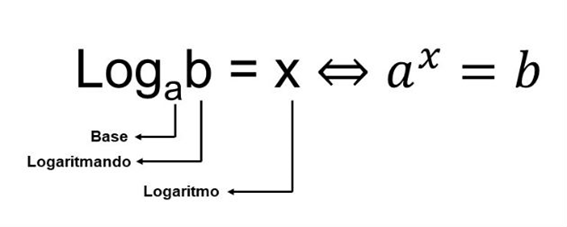
The = base, which must be greater than zero (a > 0) and different from one (a ≠ 1).
B = logarithmand, where b must be greater than zero (b > 0).
x = logarithm.
Originally, the concept of the logarithm was created by the Scottish mathematician. John Napier (1550 – 1617), in the 17th century, with the purpose of simplifying complex trigonometric calculations. The English mathematician Henry Briggs (1561 – 1630) also contributed to the studies on the logarithm, considered one of those responsible for improving this function and creating its current formation law.
Etymologically, the word "logarithm" is formed by joining two Greek terms: logos and arithmos, which mean, respectively, “reason” and “number”.
Logarithm Properties
Some of the main logarithm rules are:
- When the logarithm is equal to base, the logarithm will always be equal to 1;

- Logarithm of any base, whose logarithm is equal to 1, will always have the result equal to 0;
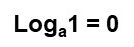
- Two logarithms with the same base are equal when the logarithms are also equal;

- A base power The and exponent equal to the logarithm of B at the base The, it's the same as B.
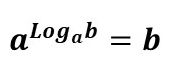
- When the logarithm is composed of a multiplication of numbers, we can separate them into a sum of logarithms with the same base for both;
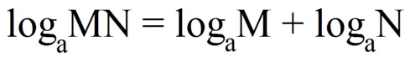
- When the logarithm is composed of a division of numbers, we can separate them in a subtraction of logarithms, with the same basis for both;
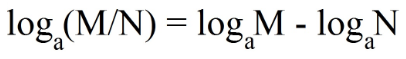
- The power rule: the logarithm of a power is simplified by multiplying the exponent by the logarithm, keeping the same base and the logarithm.

neperian logarithm
Also known as natural logarithm, consists of the logarithm with a base formed by an irrational number, called the “Euler number” (approximately equal to 2.718281…). It consists of the inverse function of the exponential function.
The Neperian logarithm refers to the name of its inventor, mathematician John Napier.
common logarithm
It is the most common model in mathematical calculations, especially in so-called logarithmic scales (calculation of pH, seismic magnitude, Richter scale, among others), and is characterized by having the base equal to 10.
The common logarithm can also be represented with the base hidden.
See also the meaning of power.
