Breathing can be defined as a process in which gas exchange takes place between the environment and the organism. This exchange is important because it guarantees the supply of oxygen for the cells to carry out their metabolic processes and the removal of carbon dioxide from the body.
There are different types of animal breathing, lung breathing being the best known. In addition to this type, we can mention branchial, cutaneous and tracheal breathing.
→ pulmonary breathing
THE lung breathing is one that occurs in animals that have lungs, two spongy organs located inside the rib cage. In this type of breathing, air enters the nasal cavities and travels towards the lungs until reaching small sacculiform structures called alveoli.
Each alveolus has a large number of capillaries around it, which allows the exchange between gases. Upon reaching the alveoli, oxygen from the air passes to the interior of the capillaries, and the carbon dioxide present in the capillaries passes to the interior of the alveoli. Carbon dioxide is then released out of the body through the nasal cavities or mouth, and oxygen is carried to the body's tissues.
Pulmonary breathing occurs in mammals, birds,reptiles and amphibians. In the latter group, lung respiration occurs together with skin respiration.
→ gill breathing
Branchial respiration is that which occurs in animals that have gills, thin structures in the shape of blades and very vascularized. The gills allow gas exchange to occur between the animal's blood and the aquatic environment, being, therefore, a structure present only in animals that live in water.
fish, some molluscs and crustaceans are examples of living beings that have gill breathing.
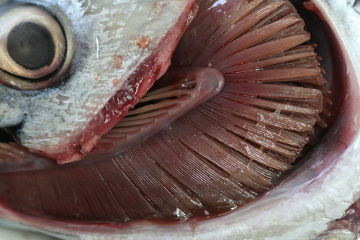
The gills guarantee the fish's breathing
→ skin breathing
Also called integumentary breathing, this type of breathing takes place on the surface of the animal's body through the skin. In this case, gas exchange occurs by diffusion and it is important that the skin is always moistened so that this process can take place properly.
Cutaneous breathing is found, for example, in flatworms,nematodes, annelids and amphibians.
→ tracheal breathing
Tracheal-type breathing occurs in animals with a respiratory organ called the trachea, which has hollow, chitinous tubes. This organ is responsible for carrying oxygen from the environment to the tissues so that gas exchange occurs in this region. In tissues, oxygen is passed directly to the cells, and carbon dioxide enters the interior of the tracheas where it follows the opposite path until it is eliminated.
Tracheal breathing occurs in some arthropods, such as insects, chilopods, millipedes and some species of spider.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/tipos-respiracao-dos-animais.htm
