The fuels used in most cars are gasoline and ethanol. The complete combustion of these two fuels generates carbon dioxide (CO2(g)) and water (H2O). Unfortunately, however, incomplete combustion and the impurities present in alcohol and gasoline can generate substances that are very polluting for the environment. In the case of gasoline, carbon monoxide (CO(g)); hydrocarbons (compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen), such as ethane (C2H6(g)); and nitrogen oxides (NOx), mainly nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2(g)).
Thus, to avoid an increase in air pollution, all cars need equipment called catalytic converter or catalytic converter, which is an anti-pollution device, which has the function of treating these gases released by the internal combustion engine and transforming them into less harmful gases. Catalytic converters are also used for this purpose in some industrial processes.
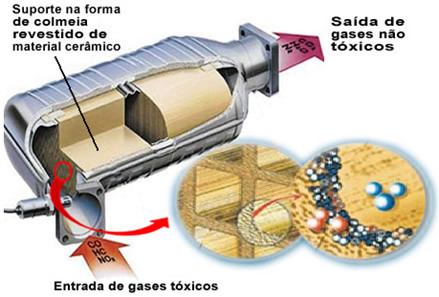
The pollutant gases mentioned leave the engine and enter the catalytic converter, passing through a kind of "hive", whose cells are generally made of ceramic or metallic material, which is coated with alumina (aluminum oxide - Al
2O3). This honeycomb shape, with tiny channels, is important because it provides a large contact surface for the gases, making them react more quickly.But the real catalyst is a metal that sits on top of aluminum oxide. Typically the metals used are palladium, rhodium, platinum or molybdenum. You can also mix these metals and use alloys. For example, in the case of gasoline, an alloy of palladium and thorium is normally used; in the case of ethanol, another alloy of palladium and molybdenum is used. These metals perform a heterogeneous catalysis with polluting gases.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
heterogeneous catalysis it is a type of reaction in which the catalyst forms with the reactants (in this case, the polluting gases) a polyphase system. This is because the catalyst adsorbs, that is, it retains the molecules of the reactants on its surface, weakening their bonds and making the reaction process faster.
As a result, catalyst metals transform polluting agents such as CO and NOx in non-toxic gases such as CO2, H2O, O2 and no2. See some of these reactions below and note that through them there is oxidation of hydrocarbons and CO (derived from incomplete combustion) and also the reduction of nitrogen oxides to nitrogen gas (N2):
2 CO(g) + 2 NO(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 1 N2(g)
2 CO(g) + 1 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g)
2C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) →4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(v)
2 NO2(g) +4 CO(g) →1 N2(g) + 4 CO2(g)
2 NO2(g) →1 N2(g) + 2 O2(g)
2 NO(g) →1 N2(g) + 1 O2(g)
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Catalytic Converter"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/conversor-catalitico.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Ozone coating that surrounds the Earth, why the ozone layer is destroyed, energy release, chlorofluorocarbons, photodecomposition of chlorofluorocarbon molecules, ozone depletion catalyst, atom of chlorine, ultraviolet rays
Chemistry

Fuel consisting of hydrocarbons, atmospheric pollutant, molecular structure of gasoline, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, incomplete combustion, catalysts, smog.