is called ion beam the size of an ion. The study of this property is dependent on knowledge about atomic radius and ions.
Atomic radius: is a measure of the size of a neutral atom (theoretical distance from the nucleus to the last electrosphere).
ions: atoms that lose (cations) or gain electrons (anions).
Protons inside the nucleus of a atom exert an attractive force on the electrons (negative particles) present in the electrospheres. The greater the number of protons, the greater this attraction and vice versa. When the number of electrons in an atom is modified by a loss or gain of these particles, the attraction between protons and electrons is modified as follows:
In the case of a cation:
The number of electrons in the electrospheres becomes less than the number of protons inside the nucleus, the which makes the attraction force of the nucleus greater, drawing the electrons closer to it. electrospheres. The result is a decrease in the radius of the atom. Thus, the radius of a cation will always be smaller than the radius of its neutral atom.
Neutral atom radius > Cation radius
In the case of an anion:
The number of electrons in the electrospheres becomes greater than the number of protons inside the nucleus. In this case, the attraction force exerted by the nucleus is overcome by the repulsion force between the electrons present in the electrospheres. The result is an increase in the radius of the atom. Thus, the radius of an anion will always be greater than the radius of its neutral atom.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Anion radius > Neutral atom radius
The two situations presented below are a good example of what happens to the radius of an ion:
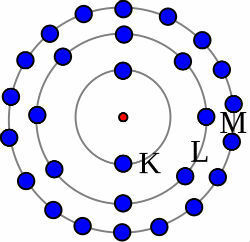
1st) Neutral Sodium Atom (11Na) and the Sodium cation (11At+)
While the neutral sodium atom has eleven protons (yellow spheres) and eleven electrons (red spheres), the sodium cation has eleven protons and ten electrons.

Sodium Neutral Atom Model
When the neutral sodium atom loses an electron, the radius decreases.
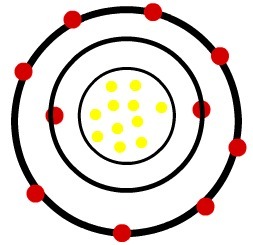
Model of a sodium cation
Observation: The third level was not represented in the image of the cation because, as it lost the only electron it had, it became empty and, therefore, was disregarded, but it is present.
2nd) Phosphorus neutral atom (15P) and the Phosphorus cation (15P-3)
While the neutral phosphorus atom has fifteen protons (yellow spheres) and fifteen electrons (red spheres), the phosphorus anion has fifteen protons and eighteen electrons.
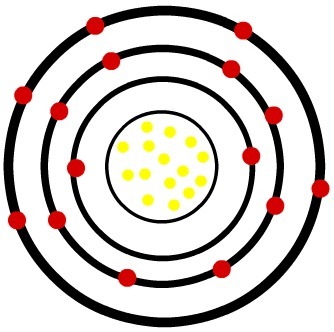
Model of a neutral phosphor atom
When the neutral phosphorus atom gains three electrons, the radius increases.
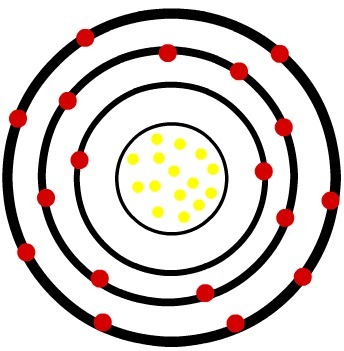
Model of an anion of the phosphor
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Ionic radius"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/raio-ionico.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.