THE animal cell is cell of type eukaryote and, therefore, presents structures such as core and cytoplasmic organelles. Some organelles make it possible to differentiate an animal cell from a plant cell. In the animal cell, the presence of lysosomes and the absence of cell wall, plastids and central vacuole or cell juice stand out.
Read too: Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Basic characteristics of an animal cell
The animal cell, like all cells, presents plasma membrane and cytoplasm. As it is a eukaryotic cell, it has a nucleus and also cell organelles. Let's explore each of these important parts of the cell next.

Plasma membrane
THE plasma membrane it is a membrane that surrounds the cell, ensuring the separation of cell contents from the external environment. It consists of a lipid bilayer, in which proteins are found associated in different ways. Some proteins extend through the lipid bilayer, while others are only attached to its surface. In addition to involving the cell, the plasma membrane has a number of other functions, such as controlling what enters and leaves the cell. This property is known as
selective permeability.Read too: What is the fluid mosaic model?
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is located, in eukaryotic cells, between the plasma membrane and the nucleus, filling the cell interior. It is in the cytoplasm that the so-called cell organelles are found and also the cytoskeleton, a complex network of proteins consisting of actin filaments, microtubules and intermediate filaments.
we call cytosol the part of the cytoplasm that is not divided by intracellular membranes, that is, the cytosol consists of the material located between the organelles. It has a gelatinous consistency, being formed by water and various gelatinous substances.
Cell organelles
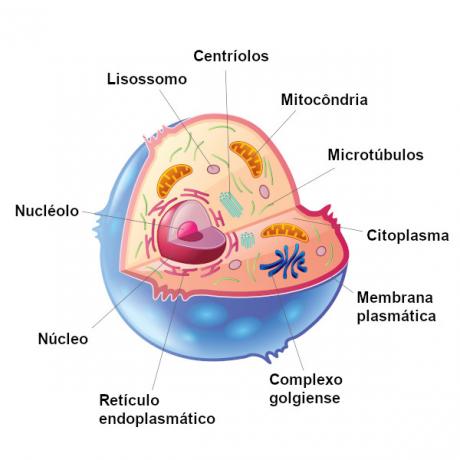
At organelles they are membrane-enclosed structures that are suspended in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells. In animal cells, we can observe the presence of the following organelles:
endoplasmic reticulum;
golgiense complex;
lysosome;
peroxisome;
mitochondria;
centrioles.
O endoplasmic reticulum can be divided into two types: smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, which are differentiated by the fact that the rough one presents ribosomes attached to its membrane. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum functions as the synthesis of lipids and detox. The rough endoplasmic reticulum, in turn, is related to the synthesis of proteins. O golgi complex, in turn, is related to modification, storage and secretion of substances.
You lysosomes are organelles related to intracellular digestion and also to the recycling of organic materials from the cell. These organelles are typical of the animal cell and are not seen in plant cells.
already the peroxisomes stand out for promoting reactions in which hydrogen peroxide is formed and degraded. This organelle is related to the oxidation of toxic molecules.
At mitochondria are extremely important organelles, being called, by many authors, of "powerhouses" of the cells. It is in the mitochondria that the cellular respiration, a process that leads to the production of ATP for the cell.
You centrioles are related to the process of cell division. They are often indicated as organelles unique to the animal cell, but they occur in most of the eukaryotic cells, not being present only in non-flagellate cells of plants, red algae and fungi.
We cannot fail to mention the ribosomes. These structures are not considered organelles by many authors, due to the absence of membranes. Its function is to carry out the protein synthesis. They are present in eukaryotic cells and also prokaryotes.
Core
O coreit is a typical structure of the eukaryotic cell, and this is where most of the cell's genetic information resides. Responsible for controlling cellular activities, it is surrounded by two membranes, which together are called nuclear wrap or caryotheque. In the nucleus we find, in addition to DNA, a region called the nucleolus, where there is a large amount of RNA. It is in the nucleolus that ribosomal subunits are formed.
Differences between plant and animal cells
THE animal cell and plant cell they are two types of eukaryotic cells, and therefore have many features in common. We can differentiate them, however, by observing the presence or absence of certain structures. Below are the main differences between these cell types.
The plant cell presents cell wall, structure absent in the animal cell.
The plant cell has some typical organelles. Plastids and cellular juice vacuole or central vacuole are not seen in animal cells.
Lysosomes are organelles found only in the animal cell.
To learn more, go to: Differences between animal and plant cells.
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/celula-animal.htm
