Hydrogenation occurs with unsaturated acyclic hydrocarbons, that is, which have open chains with double or triple bonds, such as alkenes, alkynes and dienes. It can also occur in aromatic hydrocarbons, as they have double bonds in the ring, and with cyclans (cycloalkanes) of up to five carbons.
These compounds react like hydrogen gas in the presence of some catalyst, such as nickel, platinum and palladium, under heating. Thus, an addition reaction occurs, in which the pi (π) bond is broken, forming two new single bonds and hydrogen is introduced to the molecule.
Generically, we have:
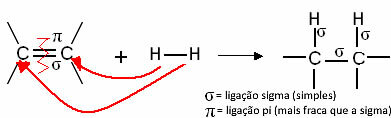
Generic hydrogenation reaction
Now let's look at some examples:
- Hydrogenation to alkenes: The product obtained is an alkane.
Below we have a hydrogenation reaction of ethylene (or ethylene) to obtain ethane:
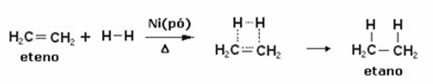
Example of an ethylene hydrogenation reaction
This type of catalytic hydrogenation is used by the food industry to make semi-solid fats such as margarines. Vegetable oils and fats differ only in that oils have long molecules with double bonds between carbons, while fats have only single bonds between their carbons.
Thus, to convert an oil into a fat, it is enough to hydrogenate the oil. That way your double bonds will be broken and converted to single bonds. The result is the production of calls hydrogenated vegetable fats.
- Alkyne hydrogenation: Since alkynes have two pi bonds, their complete hydrogenation takes place in two stages, in the first one an alkene is formed and in the second, an alkane.
In the reaction below, we have the hydrogenation of propyne with final formation of propane:
1st step: H3C C ≡ CH+ H2 → H3C CH═ ÇH2
2nd stage: H3C CH═ ÇH2 + 2 hours2 → H3C CH2─ ÇH3
If we want this reaction to stop in the 1st step, we must use some substance that interrupts the catalyst's action.
- Hydrogenation of dienes: There are three types of dienes: accumulated (double bonds appear below), isolated (double bonds are separated by at least two single bonds) and conjugates (double bonds appear alternately).
The hydrogenation of accumulated and isolated dienes occurs in the same way that we saw for alkenes, but in double, as dienes have more unsaturation. See two examples:
* Example of hydrogenation in accumulated diene:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
H H H
│ │ │
H3C CH ═ Ç ═ CH CH3 + 2 hours2 → H3C CH ─ Ç ─ CH CH3
│ │ │
H H H
* Example of hydrogenation in isolated diene:
H H H H
│ │ │ │
H3C CH ═ CH─CH2 CH ═ CH CH3 +2 H2 → H3C CH ─ CH─CH2 CH ─ CH CH3
On the other hand, the hydrogenation of conjugated dienes can happen in two ways: with 1.2 addition and 1.4 addition. The most common is the 1,2 addition, in which hydrogens are added to carbons that make the double bond and at low temperatures. The 1,4 addition, on the other hand, occurs at elevated temperatures and is when there is resonance and appearance of free valences in carbons 1 and 4. See examples of each case:
* Example of 1.2 addition in conjugated dienes:
H2C CH ─ CH ═ CH2 + H2 → H2C CH ─ C ─ CH CH2
│ │
H H
* Example of addition 1.4 in conjugated dienes:
H2C CH ─ CH ═ CH2 + H2 → H2C CH ═ CH CH2
│ │
H H
- Hydrogenation of aromatics: The pi bonds of the benzene ring are broken and the hydrogen atoms are added to the carbons that make these bonds.
This type of total hydrogenation is shown below:

Total benzene hydrogenation reaction
- Cyclan hydrogenation: Formation of an alkane occurs.
Example: Hydrogenation of cyclopropane:
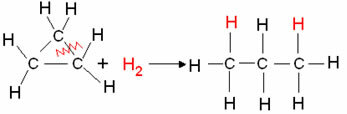
Cyclopropane hydrogenation reaction
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Organic hydrogenation reaction"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/reacao-organica-hidrogenacao.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Curiosities

How did margarine come about?, margarine, history of the emergence of margarine, award won by Hippólyte de Mége Mouriés in the year of 1869, award proposed by Napoleon's government, at a time when France was going through a serious economic crisis, several exp.


